| ID |
Date |
Author |
Type |
Subject |
|
1
|
Tue Apr 19 19:09:25 2016 |
James Bynes | Instructions | Obtaining data from XRM development boardstack | Here are the instructions to obtain data from XRM boardstack. This has currently been tested with 1 carrier board, but little modifications will allow multiple boards. Currently the data
taken is raw data, a pedestal extractor is currently under works.
The current firmware and software branch can be accessible from the svn repo at: https://www.phys.hawaii.edu/repos/belle2/itop/electronics/branches/XRM
**note** The firmware and software bundle can also be temporarily downloaded from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7Z8jduXUZ-LbFdUTFdEMkctUnc/view?usp=sharing
**note** Software bundle does not include XRM parser, please download from this ELOG.
**note** The following instructions are written using the directory for the test setup at IDLAB. Please modify the upcoming directories to match your system.
If any questions, please email James (bynes@hawaii.edu) or Luca (lucam@hawaii.edu)
Preliminary Step (setting up the network):
The firmware has been setup to communicate with a workstation using point-to-point topologies.
First, connect a SFP module from the SCROD to a media converter, then connect the Ethernet cable to your workstation.
Workstation IP
Next, we setup the test workstation (at IDLAB) using a static IP address, this machine ran Scientific Linux (red hat variant)
From red hat linux this can be done like so...
Menu System >> Administration >> Network
Statically set IP address:
Address 192.168.10.200
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
SCROD firmware IP
The firmware is currently set to use IP address 192.168.10.***
where the last 3 digits is the ID of the SCROD. This IP will come in handy when launching the communication GUI.
Step 1 (program FPGA):
First need to source Xilinx settings, if your .bashrc doesn’t already do so.
Directory: /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2014.4/
Change to c shell, type ‘csh’ in terminal
Source settings64.csh
Directory: /home/idlab/svn-02-18-2016/gigE
Upload bitfiles to FPGAs on chain ‘xmd -tcl program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl’
Step 2 (run GUI):
Directory: /home/idlab/svn-02-18-2016/gigE/software/gigE/
Source setup_env_template.csh
Now run GUI: ‘bin/develTest 192.168.10.101’
**Note** 101 is the SCROD board ID, this should be on the SCROD itself on a whitish label.
To test whether or not link to SCROD is up, from configuration tab on GUI, click “Read Configuration” button on the bottom
Step 3 (configuration):
Next, the configuration script will need to be ran
Directory: /home/idlab/svn-02-18-2016/gigE/software/gigE/pnnl
Run configuration script: './configure_boardstack.csh'
...
In the GUI, will also need to manually configure some settings.
From the Configuration tab, change the following fields to the parameters:
trigMask -> 0xe
featureExtractionMode -> Passthrough
After these two parameters are changed, hit the “Write Configuration” button on the bottom.
Step 4 (pull data):
This current script will take data from carrier 0 (includes all 4 ASICs).
Directory: /home/idlab/svn-02-18-2016/gigE/software/gigE/pnnl/
Run current test script: ‘./runtest.csh’
The binary file will be outputted to data/test_c0_1.bin
Step 5 (parse data):
XRMdataExtractor.c will convert binary data pulled from previous step and output to a readable format. It is attached to this elog
Use: ./XRMdataExtractor <binary_file>
Output files: XRM_header_from_binary_file.txt, XRM_data_from_binary_file.txt
The header file shows format of data file which is as follows:
carrier# | ASIC# | Sample# | CH0 | CH1 | CH2 | CH3 | CH4 | CH5 | CH6 | CH7
Upcoming additions:
XRMpedExtractor
XRMdataVisualizer |
| Attachment 1: XRMdataExtractor.c
|
/******************************************************************
* Author: James Bynes
* Date: 04-19-2016
* XRMdataExtractor.c
* Description: Extracts data taken from ASIC and outputs to
* readable format.
******************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
unsigned int data_ch[8][64];
int mm = 0;
int carrier = 0;
int asic = 0;
void initialize_data(void){
int m,n;
for(n=0;n<8;n++){
for(m=0;m<64;m++)
data_ch[n][m]=0;
}
}
unsigned int createMask(unsigned int a, unsigned int b){
unsigned int r=0;
unsigned int i=0;
for (i=a; i<=b; i++)
r |= 1 << i;
return r;
}
void fprint_data(FILE *fp){
int m,n;
for(m=0;m<64;m++)
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", carrier, asic, m, data_ch[0][m], data_ch[1][m], data_ch[2][m], data_ch[3][m], data_ch[4][m], data_ch[5][m], data_ch[6][m], data_ch[7][m]);
}
void get_eventInfo(FILE *headerFile, unsigned int wordsInPacket,int mm, int k){
unsigned int r, result;
fprintf(headerFile,"line %d\n", mm);
fprintf(headerFile,"k: %d\n", k);
r = createMask(30,31);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>30;
carrier = result;
fprintf(headerFile,"Carrier: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(28,29);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>28;
asic = result;
fprintf(headerFile,"IRSX: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(27,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>27;
fprintf(headerFile,"0: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(24,26);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>24;
fprintf(headerFile,"Channel: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(16,23);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
fprintf(headerFile,"LastWriteAddress: 0x%02x\n", result);
r = createMask(9,15);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>9;
fprintf(headerFile,"SCROD ID: 0x%03x\n", result);
r = createMask(0,8);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
fprintf(headerFile,"Converted Addr: 0x%03x\n", result);
}
main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(argc < 2){
printf("You must enter a binary filename\n");
goto INVALID_ARGS;
}
char headerName[80];
char dataName[80];
strcpy(headerName, "XRM_header_");
strcat(headerName, argv[1]);
strcat(headerName, ".txt");
strcpy(dataName, "XRM_data_");
strcat(dataName, argv[1]);
strcat(dataName, ".txt");
FILE *fileName = fopen(argv[1], "r");
FILE *headerFile = fopen(headerName, "w");
FILE *dataFile = fopen(dataName, "w");
fputs("DATA FORMAT\n", headerFile);
fputs("carrier# | ASIC# | Sample# | CH0 | CH1 | CH2 | CH3 | CH4 | CH5 | CH6 | CH7\n\n", headerFile);
if(!fileName){
printf("File doesn't exist\n");
INVALID_ARGS:
printf("Usage:\n");
printf("XRMdataExtractor <binary file>\n");
return;
}
unsigned int wordsInPacket, packet_hdr, result, r, num_windows, footer;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
initialize_data();
printf("_________HEADER__________\n");
while(!feof(fileName)){
NEW_EVENT:
fread(&packet_hdr, sizeof(packet_hdr),1,fileName);
if(feof(fileName))
break;
wordsInPacket = packet_hdr;
if (mm < 3){
if (mm == 0){
fprintf(headerFile,"Event size: %d\n", wordsInPacket);
}
if (mm == 1){
r = createMask(28,31);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>28;
fprintf(headerFile,"Trig Pattern: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(19,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>19;
num_windows = result+1;
fprintf(headerFile,"# of windows: 0x%03x\n", result);
r = createMask(0,18);
result = r & wordsInPacket;
fprintf(headerFile,"Timestamp: 0x%05x\n", result);
}
if (mm == 2){
get_eventInfo(headerFile,wordsInPacket,mm,k);
}
}
else{
if((j < 8) && (i < 64)){
r = createMask(0,11);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
r = createMask(16,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
}
else{
if((j==7)){ //on to next event
j = 0;
i = 0;
k = k + 1;
fprint_data(dataFile);
if(k<4)
get_eventInfo(headerFile,wordsInPacket,mm,k);
else{
footer = wordsInPacket;
printf("Footer %08x\n",footer);
mm = 0;
k = 0;
goto NEW_EVENT;
}
}
else{//on to next channel (same event)
i = 0;
j++;
r = createMask(0,11);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
r = createMask(16,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
}
}
}
mm++;
}
printf("\n");
}
|
|
2
|
Sun May 1 01:45:45 2016 |
James Bynes | Instructions | Setting up Ubuntu 14.04 to take data from XRM boardstack | This ELOG shows how to obtain data from XRM boardstack from a fresh install of Ubuntu 14.04
i) Freshly install Ubuntu 14.04
Once installation is finished, update all packages:
'sudo apt-get update'
'sudo apt-get upgrade'
'sudo apt-get update'
ii) Add a softlink so that gmake points to make:
'sudo ln -s /usr/bin/make /usr/bin/gmake'
iii) Install the following via 'sudo apt-get install <package>'
libxml2-dev
g++
libbz2-dev
libqt4-dev
python-dev
lib32z1-dev
vim
subversion
tsch
iv) Download software package and make:
Directory: /home/
'svn co https://www.phys.hawaii.edu/repos/belle2/itop/electronics/branches/XRM'
Directory: ~/XRM/software/gigE/
'source setup_env_template.sh'
'make clean'
'make' (should make with no errors)
v) Install Vivado 2014.4 using web pack (used Design edition since limited in space)
'chmod +x Xilinx_installation_file.bin'
'sudo ./Xilinx_installation_file.bin'
install to /opt/Xilinx/...
allow write permissions to Xilinx folder:
'sudo chmod 777 -R /opt/Xilinx/'
'sudo chmod 777 -R ~/.Xilinx'
Open ~/.bashrc in your favorite text editor and add the following:
____________________________________________________
XILINXD_LICENSE_FILE=<your_license>
LM_LICENSE_FILE=<your_license>
export XILINXD_LICENSE_FILE
export LM_LICENSE_FILE
source /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2014.4/settings64.sh
____________________________________________________
Now show be able to run vivado by typing vivado from xterm
vi) Setting up network for communication with boardstack:
The firmware has been setup to communicate with a workstation using point-to-point topologies.
First, connect a SFP module from the SCROD to a media converter, then connect the Ethernet cable to your workstation.
Workstation IP
From Network Connections, add a new Ethernet connection
From the Ethernet tab, select your network adapter Device MAC Address
Statically set IP address:
On IPv4 tab, select Manual from drop-down list
Click on Add and add the following:
Address: 192.168.10.200
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
SCROD firmware IP
The firmware is currently set to use IP address 192.168.10.***
where the last 3 digits is the ID of the SCROD. This IP will come in handy when launching the communication GUI.
vii) Program FPGA
Directory: ~/XRM/
Upload bitfiles to FPGAs on chain ‘xmd -tcl program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl’
viii) Run GUI
Directory: ~/XRM/software/gigE/
'Source setup_env_template.sh'
Now run GUI: ‘bin/develTest 192.168.10.101’
**Note** 101 is the SCROD board ID, this should be on the SCROD itself on a whitish label.
To test whether or not link to SCROD is up, from configuration tab on GUI, click “Read Configuration” button on the bottom
ix) Configure boardstack
Open a new terminal window and source setup_env_template.sh again
Directory: ~/XRM/software/gigE/pnnl/
Open configure_boardstack.csh with your favorite text editor
On the line 'foreach carrier(...)', starting from 0, sequential add numbers for the amount of carriers on the boardstack
Example: 'foreach carrier(0 1 2)' is used for 3 carriers on the boardstack
Save and run the file: './configure_boardstack.csh'
On the GUI from the configuration tab, change the following parameters:
trigMask -> 0xe (for 1 carrier), 0xc (for 2 carriers), 0x8 (for 3 carriers)
featureExtractionMode -> Passthrough
x) Pull Data
Directory: ~/XRM/software/gigE/pnnl/
'/.runtest.csh'
xi) Parse Data
Directory: ~/XRM/software/gigE/pnnl/data
Download file attached to this ELOG to directory
Compile: 'gcc -o XRMdataExtractor XRMdataExtractor.c'
Parse data: 'XRMdataExtractor test_c0_1.bin'
Open XRM_data_test_c0_1.bin.txt using your favorite text editor to look at the data
xii) Future Additions
XRMpedExtractor - This program will determine pedestals |
| Attachment 1: XRMdataExtractor.c
|
/******************************************************************
* Author: James Bynes
* Date: 04-19-2016
* XRMdataExtractor.c
* Description: Extracts data taken from ASIC and outputs to
* readable format.
******************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
unsigned int data_ch[8][64];
int mm = 0;
int carrier = 0;
int asic = 0;
void initialize_data(void){
int m,n;
for(n=0;n<8;n++){
for(m=0;m<64;m++)
data_ch[n][m]=0;
}
}
unsigned int createMask(unsigned int a, unsigned int b){
unsigned int r=0;
unsigned int i=0;
for (i=a; i<=b; i++)
r |= 1 << i;
return r;
}
void fprint_data(FILE *fp){
int m,n;
for(m=0;m<64;m++)
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", carrier, asic, m, data_ch[0][m], data_ch[1][m], data_ch[2][m], data_ch[3][m], data_ch[4][m], data_ch[5][m], data_ch[6][m], data_ch[7][m]);
}
void get_eventInfo(FILE *headerFile, unsigned int wordsInPacket,int mm, int k){
unsigned int r, result;
fprintf(headerFile,"line %d\n", mm);
fprintf(headerFile,"k: %d\n", k);
r = createMask(30,31);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>30;
carrier = result;
fprintf(headerFile,"Carrier: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(28,29);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>28;
asic = result;
fprintf(headerFile,"IRSX: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(27,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>27;
fprintf(headerFile,"0: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(24,26);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>24;
fprintf(headerFile,"Channel: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(16,23);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
fprintf(headerFile,"LastWriteAddress: 0x%02x\n", result);
r = createMask(9,15);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>9;
fprintf(headerFile,"SCROD ID: 0x%03x\n", result);
r = createMask(0,8);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
fprintf(headerFile,"Converted Addr: 0x%03x\n", result);
}
main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(argc < 2){
printf("You must enter a binary filename\n");
goto INVALID_ARGS;
}
char headerName[80];
char dataName[80];
strcpy(headerName, "XRM_header_");
strcat(headerName, argv[1]);
strcat(headerName, ".txt");
strcpy(dataName, "XRM_data_");
strcat(dataName, argv[1]);
strcat(dataName, ".txt");
FILE *fileName = fopen(argv[1], "r");
FILE *headerFile = fopen(headerName, "w");
FILE *dataFile = fopen(dataName, "w");
fputs("DATA FORMAT\n", headerFile);
fputs("carrier# | ASIC# | Sample# | CH0 | CH1 | CH2 | CH3 | CH4 | CH5 | CH6 | CH7\n\n", headerFile);
if(!fileName){
printf("File doesn't exist\n");
INVALID_ARGS:
printf("Usage:\n");
printf("XRMdataExtractor <binary file>\n");
return;
}
unsigned int wordsInPacket, packet_hdr, result, r, num_windows, footer;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
initialize_data();
printf("_________HEADER__________\n");
while(!feof(fileName)){
NEW_EVENT:
fread(&packet_hdr, sizeof(packet_hdr),1,fileName);
if(feof(fileName))
break;
wordsInPacket = packet_hdr;
if (mm < 3){
if (mm == 0){
fprintf(headerFile,"Event size: %d\n", wordsInPacket);
}
if (mm == 1){
r = createMask(28,31);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>28;
fprintf(headerFile,"Trig Pattern: 0x%01x\n", result);
r = createMask(19,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>19;
num_windows = result+1;
fprintf(headerFile,"# of windows: 0x%03x\n", result);
r = createMask(0,18);
result = r & wordsInPacket;
fprintf(headerFile,"Timestamp: 0x%05x\n", result);
}
if (mm == 2){
get_eventInfo(headerFile,wordsInPacket,mm,k);
}
}
else{
if((j < 8) && (i < 64)){
r = createMask(0,11);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
r = createMask(16,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
}
else{
if((j==7)){ //on to next event
j = 0;
i = 0;
k = k + 1;
fprint_data(dataFile);
if(k<4)
get_eventInfo(headerFile,wordsInPacket,mm,k);
else{
footer = wordsInPacket;
printf("Footer %08x\n",footer);
mm = 0;
k = 0;
goto NEW_EVENT;
}
}
else{//on to next channel (same event)
i = 0;
j++;
r = createMask(0,11);
result = (r & wordsInPacket);
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
r = createMask(16,27);
result = (r & wordsInPacket)>>16;
data_ch[j][i] = result;
i++;
}
}
}
mm++;
}
printf("\n");
}
|
|
3
|
Tue May 3 08:11:06 2016 |
M. Andrew | documentation | what was done in January 2016 | Here is a data dump of everything that happened on the asus laptop while getting the laste 2015 / early 2016 incarnation of the XRM tested before being delivered to KEK on the weekend of January 24th. Everything was done in bash and the firmware only addressed one carrier at a time, so the purpose of this elog entry is simply to archive the information. |
| Attachment 1: howtogetdata.mza
|
gige2
cd ..
source setup_env_template.sh
cd ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
car=0
asic=3
FB=110
python ../scripts_mod/irsxSetCarrierOn_Cal.py $car 0
./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
./setupAsic_CA.sh $car $asic $FB
rm data.bin myEvent_sub.txt ccc?
../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin pedfile_0.txt > myEvent_sub.txt
./generate_all_channels.sh
vim ccc7
gnuplot
|
| Attachment 2: 2016-01-24.XRM-history
|
375 ls -lart data
376 ls -lart data
377 ls -lart data.first-board-stack/
378 ls -lart data.first-board-stack/
379 ls -lart data
380 ls -lart data
381 ls -lart data
382 ls -lart data
383 ls -lart data
384 ls -lart data
385 ls -lart data
386 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
387 ls -lart data
388 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
389 ls -lart data
390 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
391 vim data/carrier0.asic1.pedestals
392 ls -lart data
393 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
394 less data/carrier0.asic3.pedestals
395 less data/carrier0.asic2.pedestals
396 ls -lart data
397 rm data/carrier1.asic3.pedestals data/carrier0.asic0.pedestals
398 ls -lart data
399 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
400 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
401 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
402 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
403 mv data data.after-getting-the-script-to-work
404 mkdir data
405 cd data
406 ls -lart
407 rm carrier0.asic0.pedestals
408 ls -lart
409 ls -lart
410 ls -lart
411 ls -lart ../data.after-getting-the-script-to-work/
412 ls -lart
413 ls -lart
414 ls -lart
415 ls -lart
416 ls -lart
417 ls -lart
418 ls -lart
419 ls -lart
420 ls -lart
421 ls -lart
422 cd ..
423 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
424 ls -lart
425 ls -lart data
426 ls -lart data
427 ls -lart data
428 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
429 mv data data.after-fixing-some-shorts
430 mkdir data
431 cd data
432 ls
433 ls -lart
434 rm *
435 ls -lart
436 ls -lart
437 ls -lart
438 cd ..
439 gnuplot ~/bin/mza.gnuplot
440 ssh --help
441 20start
442 fpga2
443 arp
444 vim ~/.bashrc
445 . ~/.bashrc
446 arp
447 arp
448 cd ../build/uh-svn-repo/trunk/
449 svn update
450 ls
451 cd ../branches/gigE/
452 cat program-bit-and-elf-and-go
453 head program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
454 grep freq program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
455 gige2
456 ls data -lart
457 cd ~/build/uh-svn-repo
458 svn update --revision 1041
459 svn status
460 svn diff branches/gigE/program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
461 cd ..
462 rm -rf uh-svn-repo
463 vim checkout
464 ./checkout
465 cd uh-svn-repo/trunk/software/PS7/CarrierRevE/
466 cd s
467 cd src/
468 vim CarrierRevE_main.c
469 vim CarrierRevE_main.c
470 svn dif
471 svn diff
472 cd ..
473 cd ..
474 cd ..
475 cd ..
476 cd firmware
477 mkdir build
478 cd targets/ScrodRevB_b2tt
479 make sdk_gui
480 make sdk
481 make
482 ls -lart
483 ssh xtd2
484 ssh xtd2
485 vim ~/.ssh/config
486 ssh xtd2
487 vim ~/.ssh/config
488 vim ~/.ssh/config
489 ssh xtd2
490 vim ~/.ssh/config
491 ssh xtd2
492 ssh xtd2
493 ssh xtd2
494 ssh xtd2
495 cd build/
496 vim checkout
497 ./checkout
498 cd uh-svn-repo.1143/trunk/software/PS7/Scrod/src/
499 vim main.c
500 ls -lart
501 du LaserBranch/
502 tar cf 2016-01-24.XRM.tar bin/mza.gnuplot bin/grab_all_peds LaserBranch/
503 ls -lart
504 du LaserBranch/
505 du --ma=1 LaserBranch/
506 du --ma=1 LaserBranch/software/
507 du --ma=1 LaserBranch/software/gigE/
508 du --ma=1 LaserBranch/software/gigE/ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
509 rm 2016-01-24.XRM.tar
510 tar cf 2016-01-24.XRM.tar bin/mza.gnuplot bin/grab_all_peds LaserBranch/
511 ls -lart
512 du --ma=1 LaserBranch/software/gigE/ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
513 ls -larS LaserBranch/software/gigE/ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
514 mkdir ~/data/XRM/ccc
515 mv ccc* ~/data/XRM/ccc/
516 cd LaserBranch/software/gigE/ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
517 mv ccc* ~/data/XRM/ccc/
518 ls -larS
519 mv myEvent_sub.txt myData_2000.bin sine_2000.bin myDat_2000.bin ~/data/XRM/ccc/
520 ls -larS
521 cd ..
522 du
523 ls -larS
524 du --ma=1
525 cd ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
526 du
527 mv powerDisCon/ firstRF/ pwrSigDisCon/ ~/data/XRM/ccc/
528 ls -larS
529 du
530 cd ..
531 cd ..
532 du
533 cd ..
534 du bitfiles/
535 cd bitfiles/
536 mkdir ~/bitfiles
537 ls -lart
538 head ../program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
539 head ../program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl -n 20
540 ls -lart
541 ls -lart
542 du
543 cd ..
544 du
545 cd ..
546 rm 2016-01-24.XRM.tar
547 history | grep tar
548 tar cf 2016-01-24.XRM.tar bin/mza.gnuplot bin/grab_all_peds LaserBranch/
549 ls -lart
550 cd LaserBranch/
551 find | grep elf$
552 cd ps_files/
553 du
554 cd
555 scp 2016-01-24.XRM.tar idlab:
556 rm 2016-01-24.XRM.tar
557 tar cf 2016-01-24.XRM.tar bin/mza.gnuplot bin/grab_all_peds LaserBranch/ howtogetdata.txt
558 scp 2016-01-24.XRM.tar idlab:
559 find /opt/Xilinx/SDK/ | grep settings64
560 rm 2016-01-24.XRM.tar
561 tar cf 2016-01-24.XRM.tar bin/mza.gnuplot bin/grab_all_peds LaserBranch/ howtogetdata.txt
562 scp 2016-01-24.XRM.tar idlab:
563 fpga2
564 gige2
565 ls myDat_2000.bin
566 ls -lart
567 ls -lart
568 ls -lart
569 less myDat_2000.bin
570 less myDat_2000.bin
571 ls -lart
572 rm myDat_2000.bin
573 ls -lart
574 ls -lart
575 ls -lart
576 ls -lart
577 ls -lart
578 ls -lart
579 ls -lart
580 ls -lart
581 ls -lart
582 cat howtogetdata.txt
583 grab_all_peds
584 cd data
585 ls
586 ls -lart
587 cd ..
588 mv data data.junk
589 vim ~/bin/grab_all_peds
590 mkdir ~/data/XRM
591 mkdir ~/data/XRM/data
592 vim ~/bin/grab_all_peds
593 mv data.junk/ data.boardstack-installed-in-box/ ~/data/XRM/
594 du
595 grab_all_peds
596 grab_all_peds
597 ls -lart
598 ls -lart
599 ls -lart ~/data/XRM/data
600 ls -lart
601 ls -lart
602 ls -lart
603 ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin pedfile_0.txt > myEvent_sub.txt
604 ./generate_all_channels.sh
605 ls -lart
606 gnuplot
607 less ccc0
608 less myPed_2000.bin
609 vim ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray
610 less data.bin
611 hexdump data.bin | less
612 cp ~/data/XRM/data/carrier0.asic3.pedestals peds
613 ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin peds > myEvent_sub.txt
614 ./generate_all_channels.sh
615 ls -lart
616 gnuplot
617 less ccc7
618 gnuplot
619 less ccc7
620 gnuplot
621 less ccc7
622 vim ccc7
623 gnuplot
624 vim ccc6
625 vim ccc5
626 vim ccc6
627 mv data.txt data7.txt
628 gnuplot
629 vim ccc5
630 gnuplot
631 cd ~/data/XRM/data
632 ls -lart
633 cd ../ccc/
634 ls -lart
635 gnuplot
636 cd -
637 ls -lart
638 cd -
639 gige@
640 gige2
641 ls
642 cat ~/bin/grab_all_peds
643 source setup_env_template.sh
644 cd ..
645 source setup_env_template.sh
646 cat ~/bin/grab_all_peds
647 cd ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing/
648 car=0
649 asic=3
650 FB=110
651 python ../scripts_mod/irsxSetCarrierOn_Cal.py $car 0
652 ./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
653 ./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
654 ./setupAsic_CA.sh $car $asic $FB
655 ls -lart
656 ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin pedfile_0.txto > myEvent_sub.txt
657 ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin pedfile_0.txt > myEvent_sub.txt
658 ./generate_all_channels.sh generate_all_channels.sh
659 ./generate_all_channels.sh
660 ls -lart
661 gnuplot
662 gnuplot
663 mv ccc6 ccc6.sine
664 mv ccc7 ccc7.sine
665 history
666 ../bin/MyConvertData_fullArray data.bin pedfile_0.txt > myEvent_sub.txt
667 ./generate_all_channels.sh
668 ls -lart
669 gnuplot
670 ls -lart
671 rm data.bin
672 rm ccc?
673 ls -lart
674 rm myEvent_sub.txt
... 201 more lines ...
|
| Attachment 3: 2016-01-24.XRM-code-chanes.patch
|
Index: CarrierRevE/images/CarrierRevE_PS_app_E0000001.elf
===================================================================
Cannot display: file marked as a binary type.
svn:mime-type = application/octet-stream
Index: CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE.h
===================================================================
--- CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE.h (revision 1143)
+++ CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE.h (working copy)
@@ -13,6 +13,10 @@
#define GPIO_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XGPIOPS_0_DEVICE_ID
//#define CLK_FAN_RST_N_PIN 48
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1 16 // gain stage 1
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2 19 // gain stage 2
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3 18 // gain stage 3
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4 43 // attenuator
#define SPI_CLOCK0_PIN 16 //MIO16 FOR SPI CLOCK
#define SPI_MOSI0_PIN 21 //MIO17 FOR SPI MOSI
#define SPI_CS0_PIN 18 //MIO18 FOR SPI CS0 (fanout clock)
Index: CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE_main.c
===================================================================
--- CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE_main.c (revision 1143)
+++ CarrierRevE/src/CarrierRevE_main.c (working copy)
@@ -83,10 +83,10 @@
//bool temperatureAlert = regThermStatus & 0x1;
// Debug pins
- XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 46, (carrierId & 0x1) >> 0);
- XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 47, (carrierId & 0x2) >> 1);
- XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 48, (carrierId & 0x4) >> 2);
- XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 49, (carrierId & 0x8) >> 3);
+ //XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 46, (carrierId & 0x1) >> 0);
+ //XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 47, (carrierId & 0x2) >> 1);
+ //XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 48, (carrierId & 0x4) >> 2);
+ //XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, 49, (carrierId & 0x8) >> 3);
// Check control signals in from PL
// If they've changed then write out new values to devices
u32 AsicRegEnNew = Xil_In32(AXI_ASIC_REG_EN_ADDR);
@@ -163,17 +163,23 @@
/***********************FUNCTION DEFINITIONS*****************************/
void GPIO_init(u16 DeviceId){
-
XGpioPs_Config *ConfigPtr;
-
//Initialize the GPIO driver.
ConfigPtr = XGpioPs_LookupConfig(GPIO_DEVICE_ID);
XGpioPs_CfgInitialize(&Gpio, ConfigPtr, ConfigPtr->BaseAddr);
-
}
void GPIO_pins(void){
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 1); // enables the output driver
+
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, SPI_CLOCK0_PIN, 1); //set SPI0 as output direction
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, SPI_CLOCK0_PIN, 1); //enables the output for the SPI0
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, SPI_MOSI0_PIN, 1); //set MOSI as output direction
@@ -193,6 +199,7 @@
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, 51, 0);
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, 51, 0);
+/*
//Debugging (using JTAG as GPIO)
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, 46, 1);
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, 46, 1);
@@ -202,6 +209,7 @@
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, 48, 1);
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, 49, 1);
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, 49, 1);
+*/
//Set direction and output enables for ASIC amp enables
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, AMP_ASIC0_PIN, 1);
@@ -280,6 +288,11 @@
void GPIO_defaults(void){
int cal_channel = 0;
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 0x0);
+
// Leave these disabed by default
AMP_ASIC1_LO;
AMP_ASIC2_LO;
Index: Scrod/src/main.c
===================================================================
--- Scrod/src/main.c (revision 1143)
+++ Scrod/src/main.c (working copy)
@@ -11,9 +11,15 @@
#include "feature_extraction.h"
#include "PL_AXI_REG.h"
#include "i2c.h"
+#include "xgpiops.h" //PS GPIO
+#include "xil_io.h"
#define RAW_DATAFORMAT_CARRIER 1 // assumes carrier format for raw data
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1 16 // gain stage 1
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2 19 // gain stage 2
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3 18 // gain stage 3
+#define XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4 43 // attenuator
#ifdef RAW_DATAFORMAT_CARRIER
@@ -28,8 +34,18 @@
int dataTransferOn = 0;
#define WAVE_BUFFER_SIZE 600 // Needs to stay below 6-7 MB
+#define GPIO_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XGPIOPS_0_DEVICE_ID
+XGpioPs Gpio; //driver instance for GPIO device
+
+/***********************FUNCTION DEFINITIONS*****************************/
+void GPIO_init(u16 DeviceId){
+ XGpioPs_Config *ConfigPtr;
+ //Initialize the GPIO driver.
+ ConfigPtr = XGpioPs_LookupConfig(GPIO_DEVICE_ID);
+ XGpioPs_CfgInitialize(&Gpio, ConfigPtr, ConfigPtr->BaseAddr);
+}
+
int main() {
-
u32 returnval;
volatile u32 featureExtractionMode;
@@ -38,6 +54,24 @@
init_platform();
print("Hello World\n\r");
+ GPIO_init(GPIO_DEVICE_ID);
+ //GPIO_pins();
+ //GPIO_defaults();
+
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 1); // enables the output driver
+ XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 1); // set as output direction
+ XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 1); // enables the output driver
+
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST1, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST2, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST3, 0x0);
+ XGpioPs_WritePin(&Gpio, XRM_ARP_SELECT_ST4, 0x0);
+
// Circular Waveform Buffer Init
RawWaveformCarrier_t *g_waveBuffer = (RawWaveformCarrier_t*) memalign(4096,sizeof(RawWaveformCarrier_t) * WAVE_BUFFER_SIZE); // compiler has issues with large static arrays (~8MB), so dynamically just to be safe
if(g_waveBuffer == NULL){
|
| Attachment 4: XRM-fpga2-alias-output
|
****** Xilinx Microprocessor Debugger (XMD) EngineExecuting user script : program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
last device in programming chain is number 2
It appears that you have 0 carriers connected.
****** XMD v2014.4
**** SW Build 1071353 on Tue Nov 18 16:34:53 MST 2014
** Copyright 1986-2014 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Configuring Device 2 (xc7z045) with Bitstream -- bitfiles/ScrodRevB_b2tt_gigE_B000000E.bit
....................10...................20...................30....................40...................50...................60....................70...................80...................90....................Done
Successfully downloaded bit file.
JTAG chain configuration
--------------------------------------------------
Device ID Code IR Length Part Name
1 4ba00477 4 arm_dap
2 23731093 6 xc7z045
Processor Reset .... DONE
Downloading Program -- ps_files/Scrod_PS_app_B0000007.elf
section, .text: 0x00100000-0x00106c97
section, .init: 0x00106c98-0x00106caf
section, .fini: 0x00106cb0-0x00106cc7
section, .rodata: 0x00106cc8-0x00106e83
section, .data: 0x00106e88-0x00107abb
section, .eh_frame: 0x00107abc-0x00107abf
section, .mmu_tbl: 0x00108000-0x0010bfff
section, .init_array: 0x0010c000-0x0010c007
section, .fini_array: 0x0010c008-0x0010c00b
section, .bss: 0x0010c00c-0x0010c0cf
section, .heap: 0x0010c0d0-0x0110c0cf
section, .stack: 0x0110c0d0-0x0112d8cf
Download Progress..10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.90.Done
Setting PC with Program Start Address 0x00100000
RUNNING> Processor started. Type "stop" to stop processor
|
| Attachment 5: grab_all_peds
|
#!/bin/bash -e
# 2016-01-23 mza for XRM
declare destination="${HOME}/data/XRM/data"
#. ${HOME}/.bashrc
cd /home/idlab/LaserBranch/software/gigE/
source setup_env_template.sh
cd ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing
#gige2
car=0
asic=1
FB=110
#for car in $(seq 0 2); do
# for asic in $(seq 0 3); do
filename="${destination}/carrier${car}.asic${asic}.pedestals"
echo -n "${filename}"
if [ -e "${filename}" ]; then
echo " - found"
continue
else
#touch "${filename}"
echo
fi
python ../scripts_mod/irsxSetCarrierOn_Cal.py $car 0
./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
./set_all_thresholds.sh $car $asic 0
./setupAsic_CA.sh $car $asic $FB
mv pedfile_RMS_0.txt "${filename}"
ls -lart "${filename}"
# done
#done
|
| Attachment 6: mza.gnuplot
|
# 2016-01-23 mza for XRM
plot "data/carrier0.asic0.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier0.asic1.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier0.asic2.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier0.asic3.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier1.asic0.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier1.asic1.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier1.asic2.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier1.asic3.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier2.asic0.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier2.asic1.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier2.asic2.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
plot "data/carrier2.asic3.pedestals" using ($0):($4)
pause -1
|
| Attachment 7: IMG_1025.JPG
|

|
| Attachment 8: IMG_1027.JPG
|
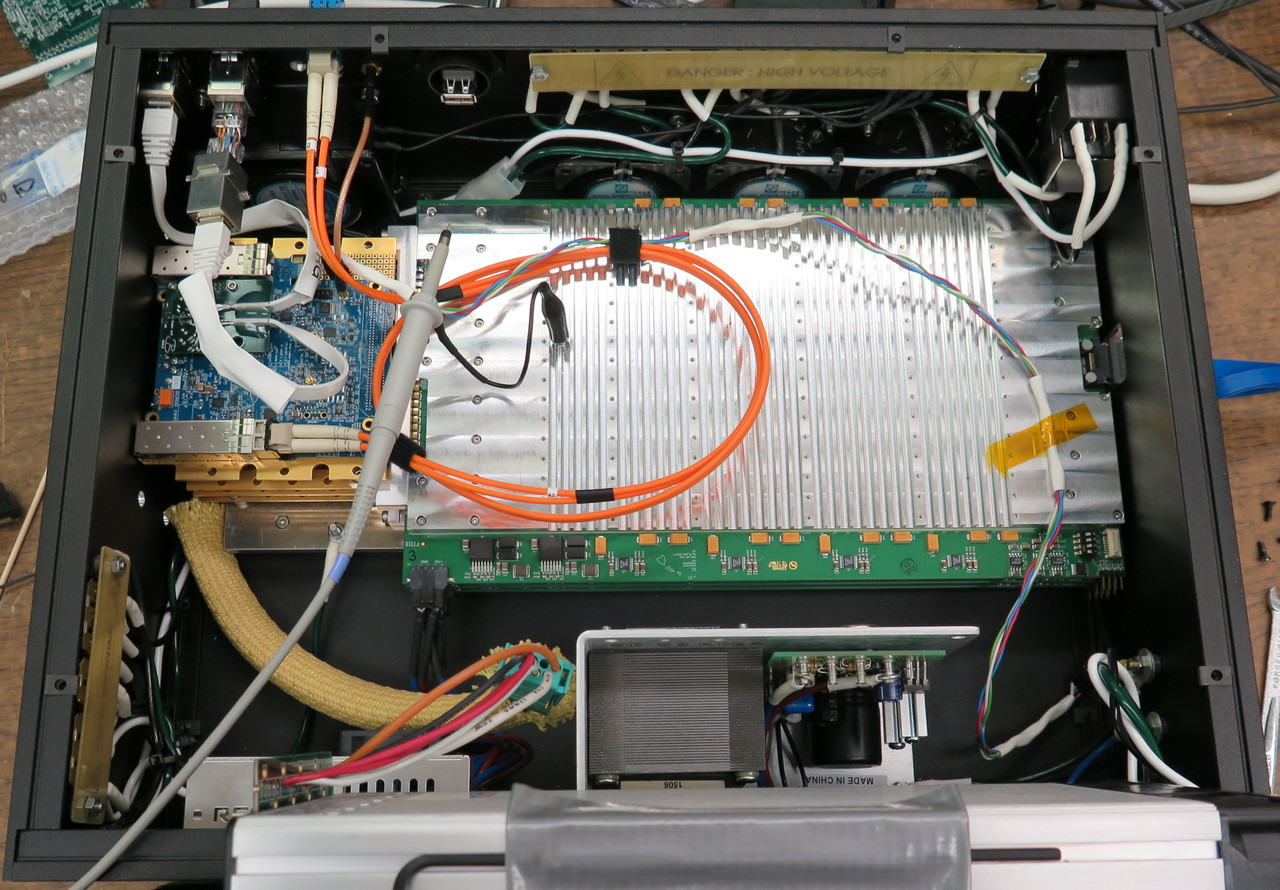
|
| Attachment 9: IMG_1028.JPG
|
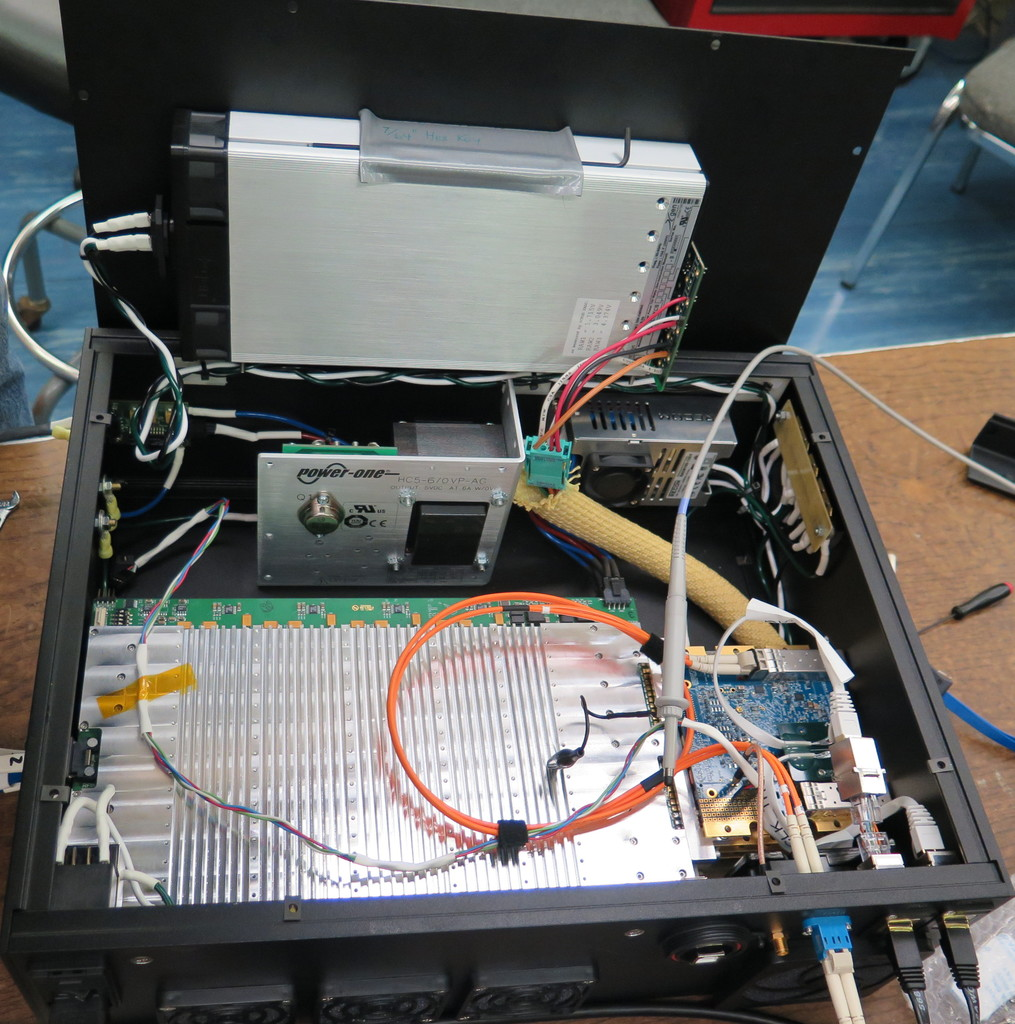
|
| Attachment 10: 2016-01-24.LASER5.png
|
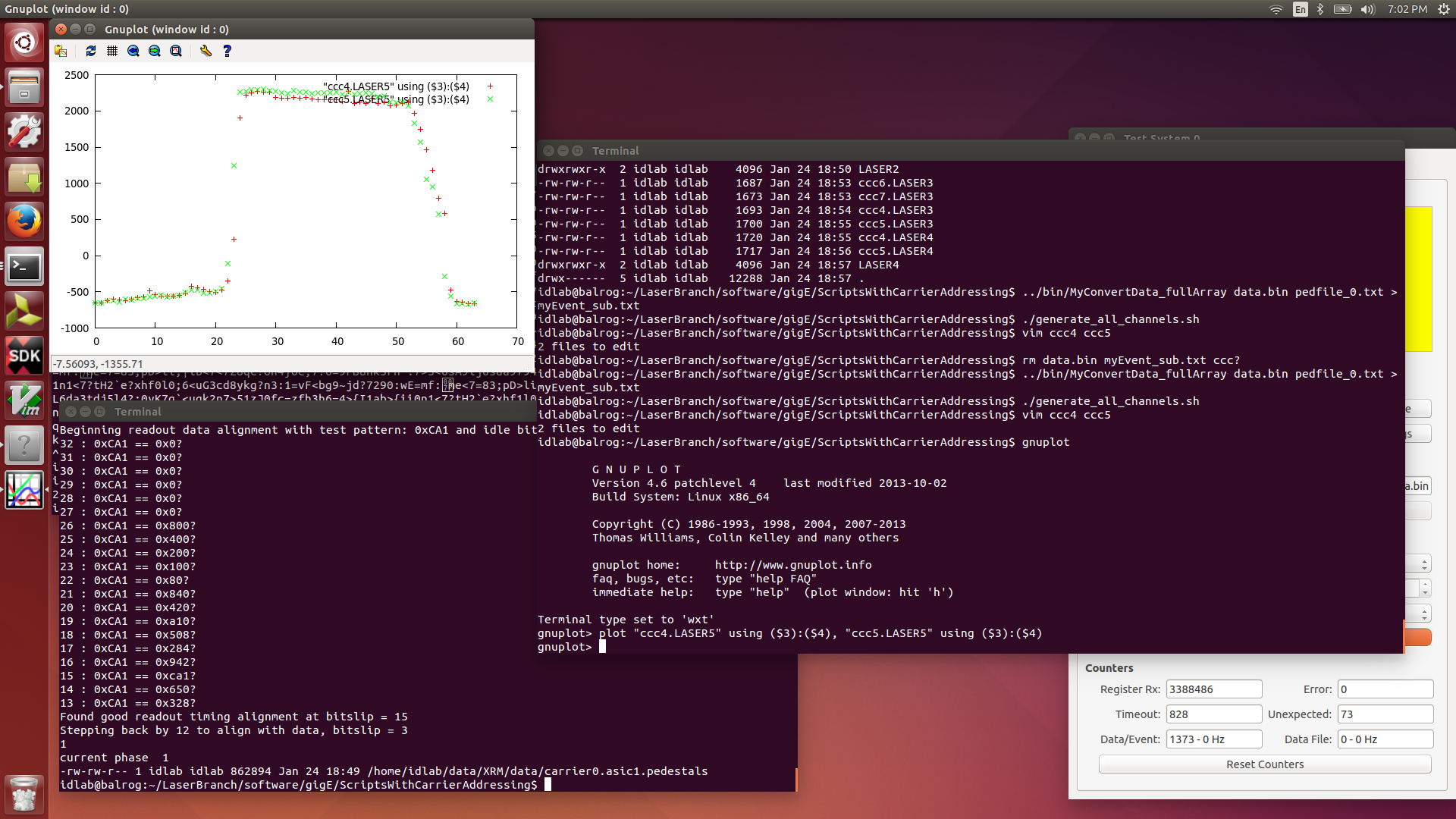
|
| Attachment 11: 2016-01-24.LASER.png
|
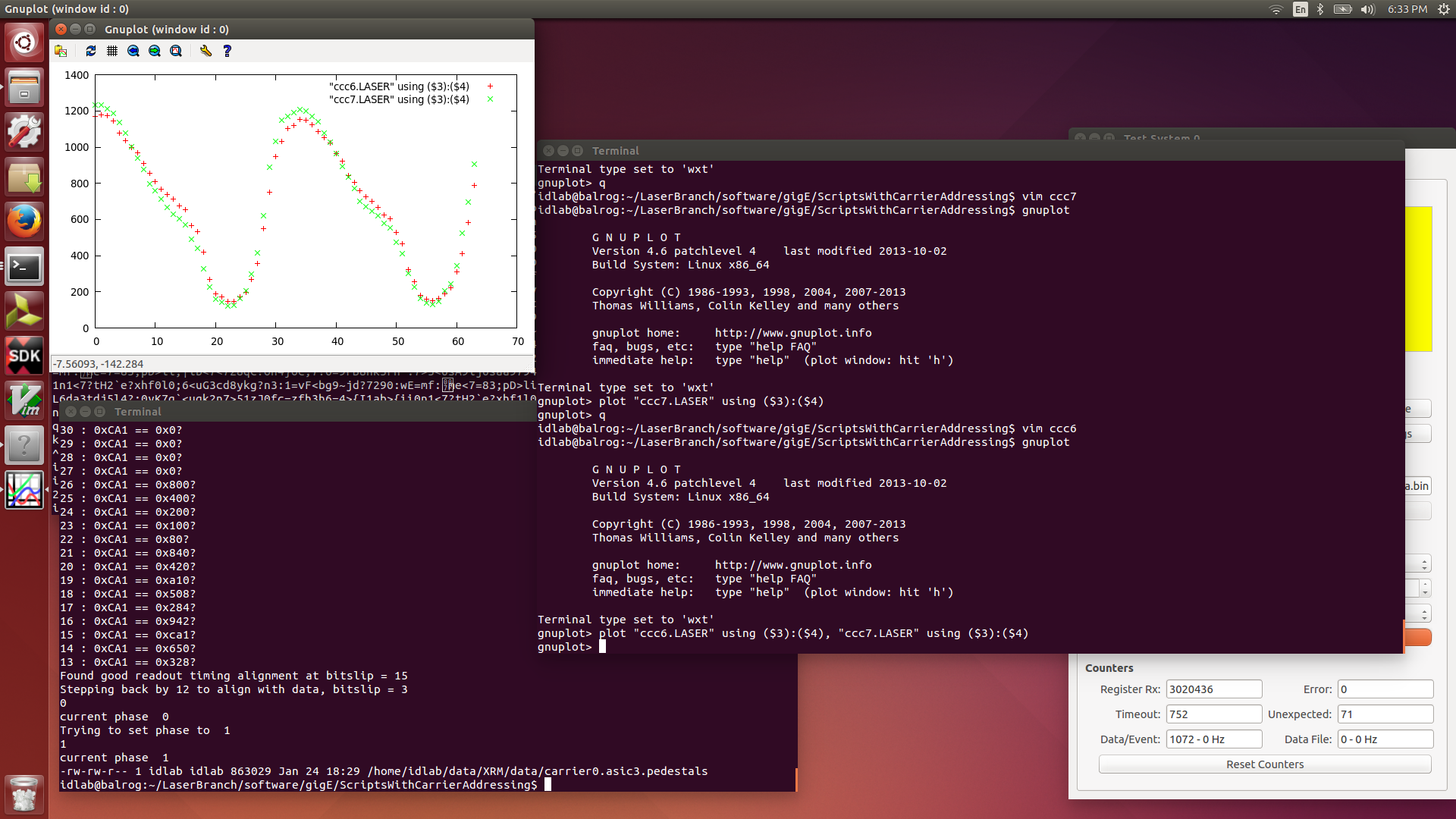
|
| Attachment 12: 2016-01-24.LASER14.png
|
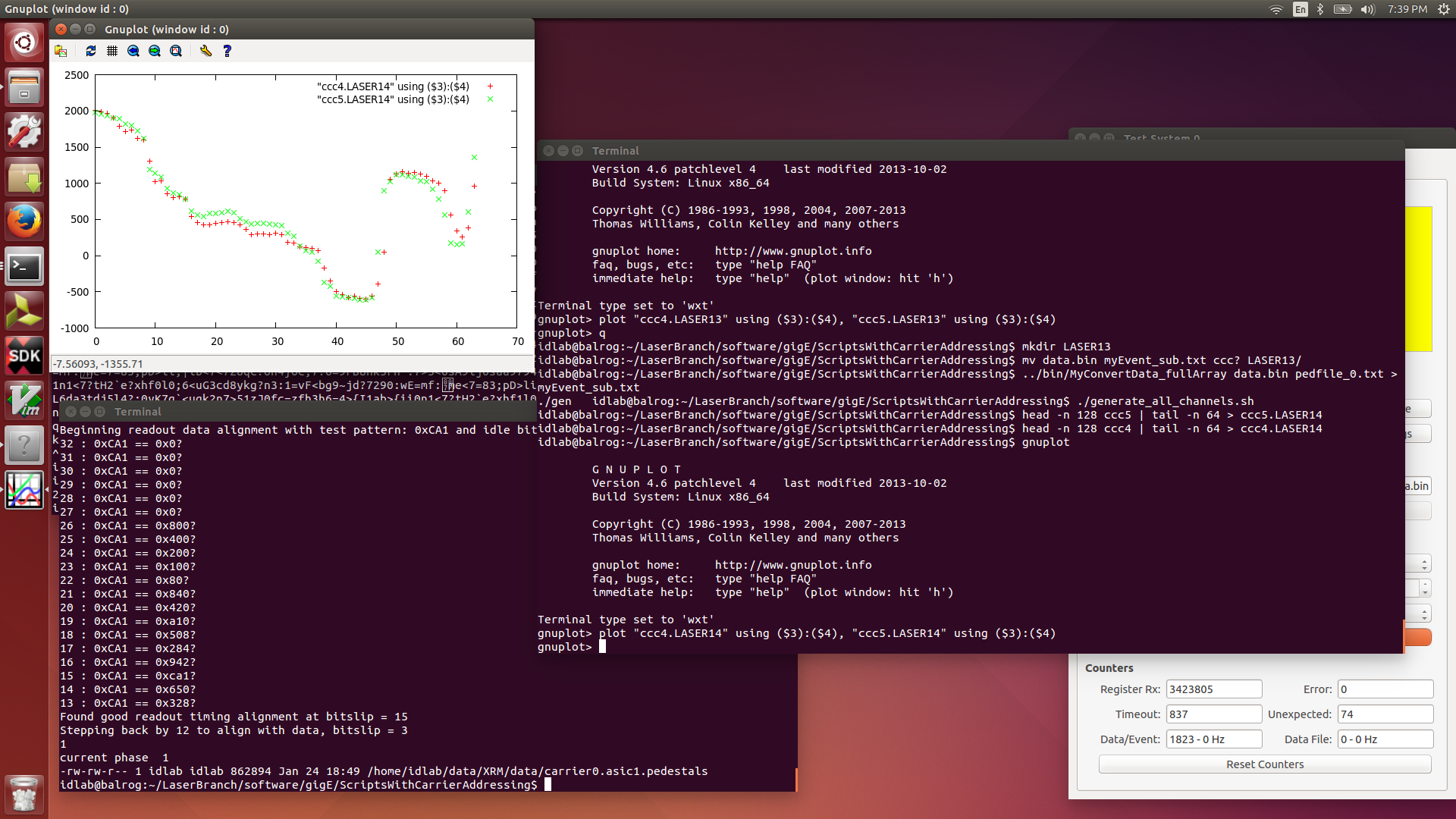
|
| Attachment 13: 2016-01-24.LASER13.png
|
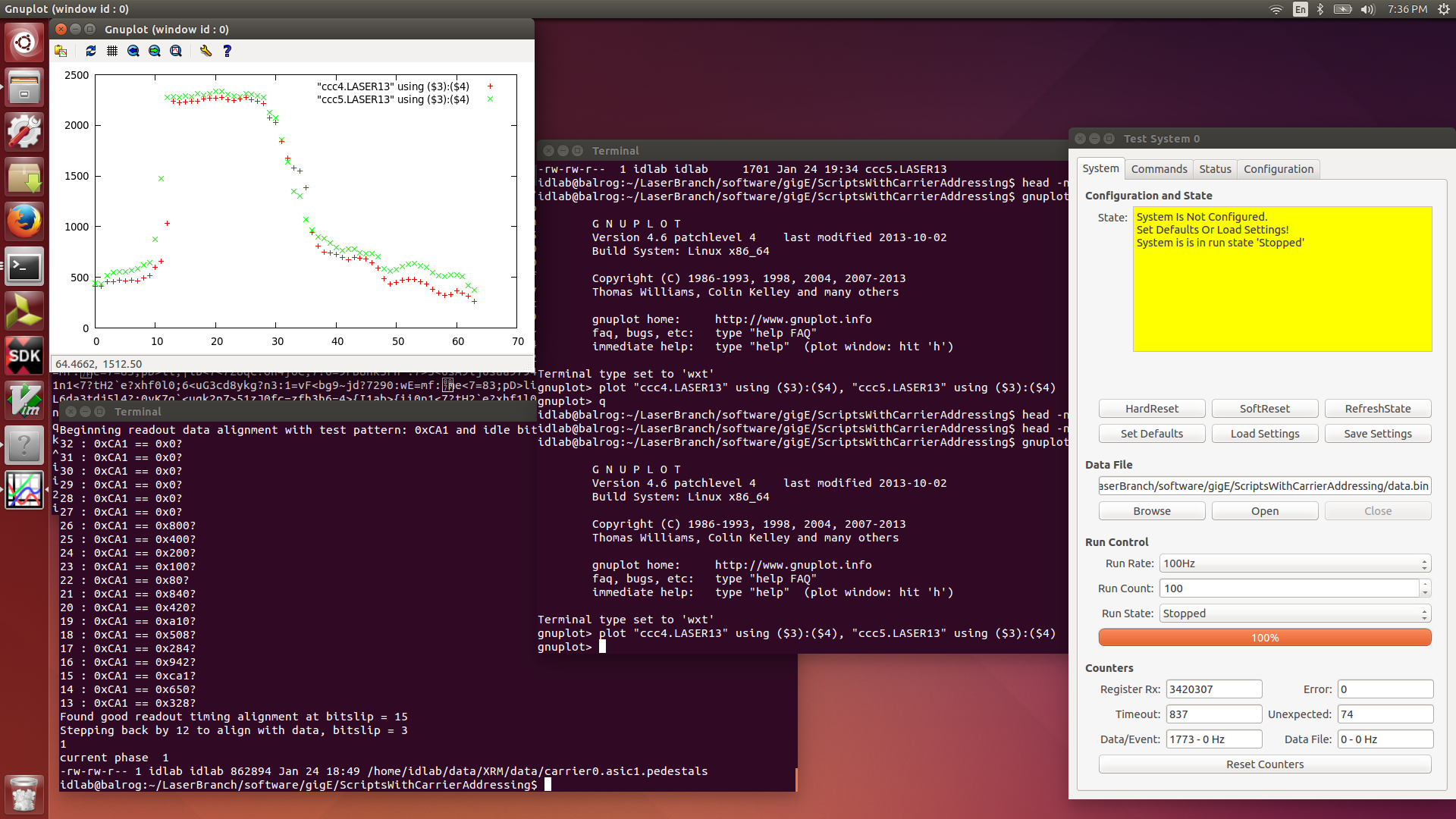
|
| Attachment 14: 2016-01-24.LASER12.png
|
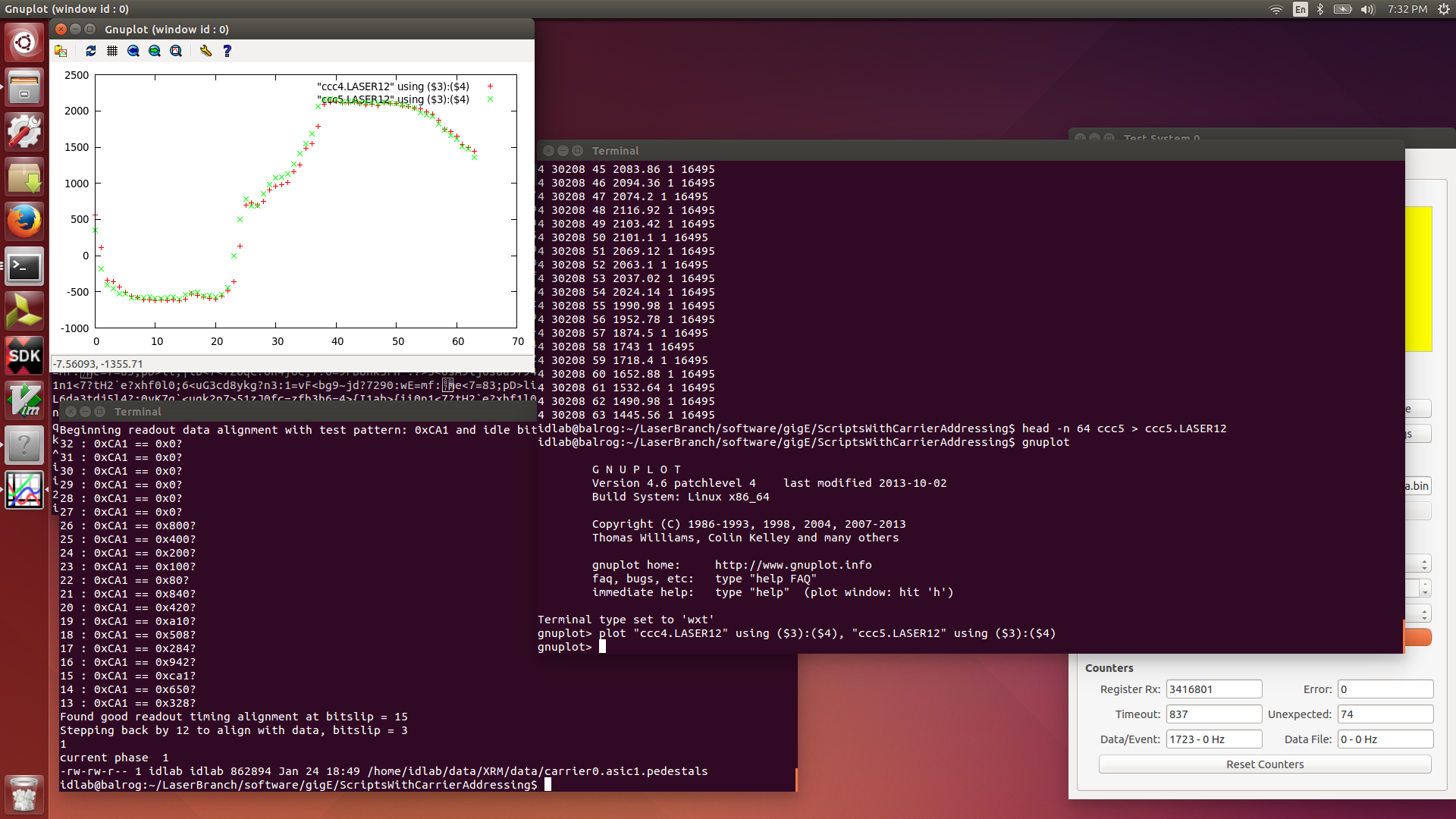
|
| Attachment 15: 2016-01-24.LASER11.png
|
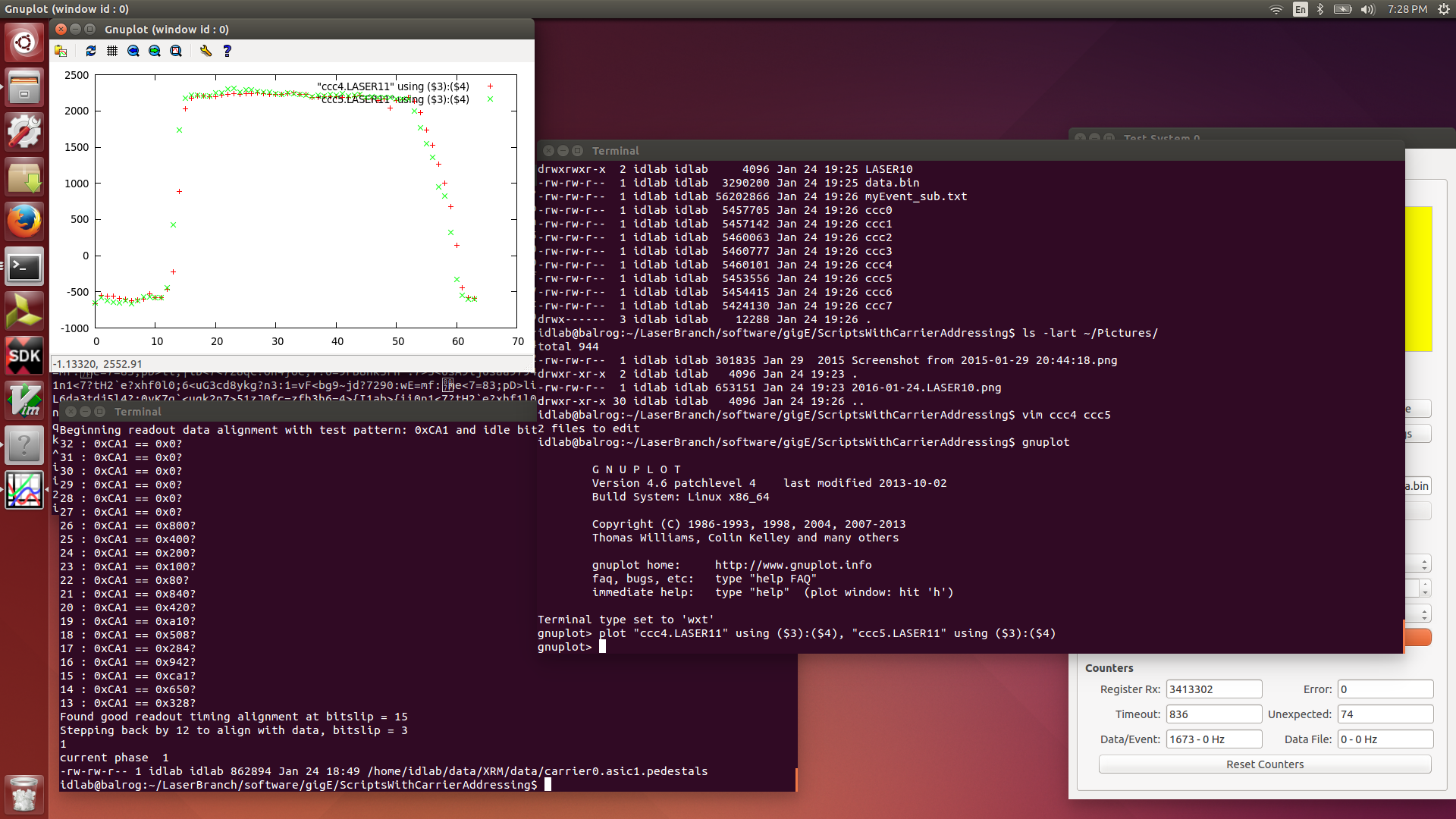
|
| Attachment 16: 2016-01-24.LASER9.png
|
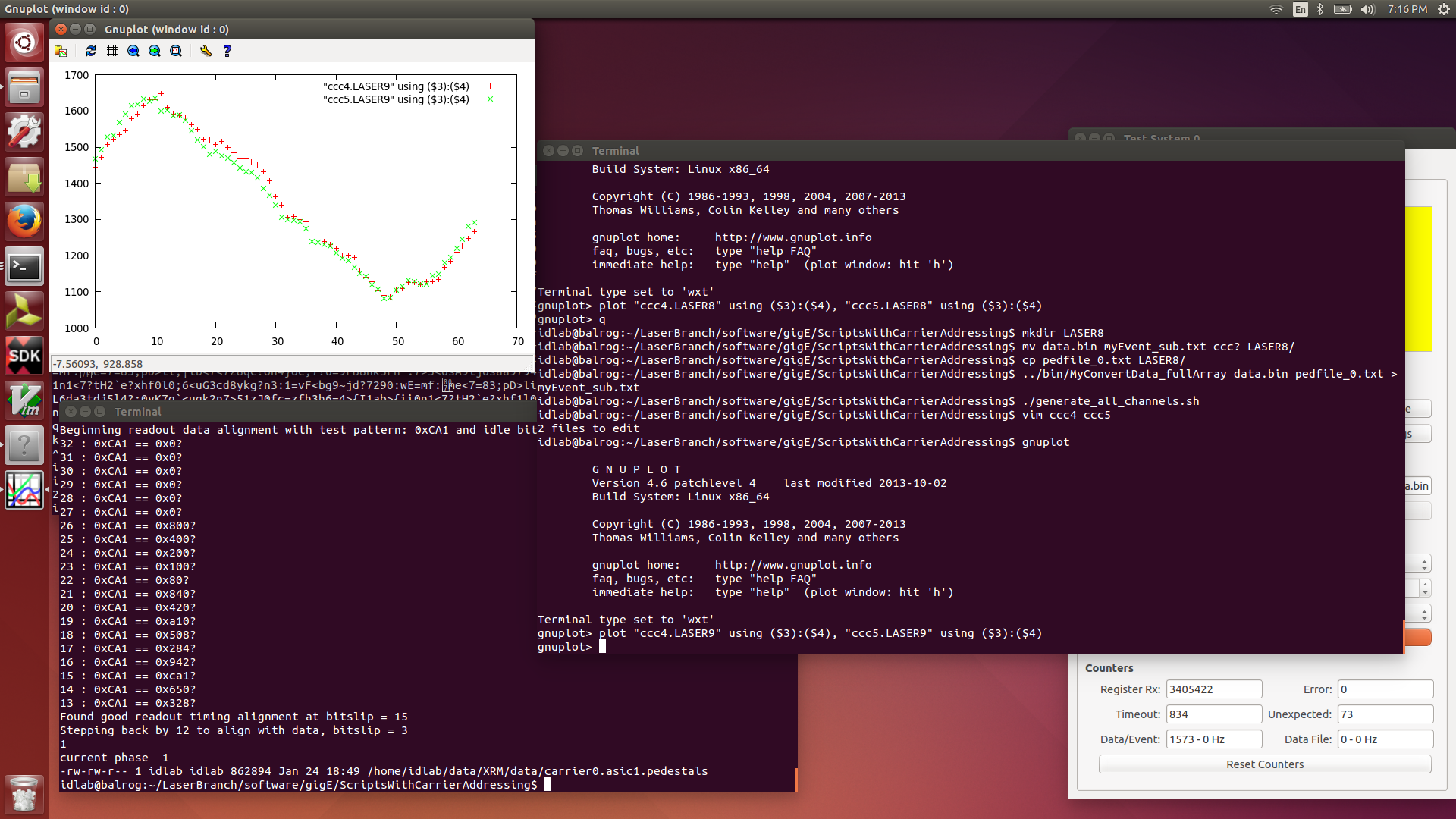
|
| Attachment 17: program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl
|
# Set for local JTAG access
# Modify for remote access via hw_server or vcse_server
set TCP "127.0.0.1:3121"
#set freq 3000000
set freq 10000000
#set TCP "ppa-linuxtest3.slac.stanford.edu:3121"
# Set current version numbers of firmware
set SCROD_FW_VERSION "B000000E"
#set SCROD_FW_VERSION "B0000009"
#Laser Test Golden File below!!!
set CARRIER_FW_VERSION "E000000B"
#Lynn's speedup improvements
#set CARRIER_FW_VERSION "E000000C_3"
#set CARRIER_FW_VERSION "E0000008"
# Set current version numbers of elf files
#set SCROD_ELF_VERSION "B0000003"
set SCROD_ELF_VERSION "B0000007"
#set CARRIER_ELF_VERSION "E0000000"
set CARRIER_ELF_VERSION "E0000001"
# Devices on the chain should enumerate as:
#
#JTAG chain configuration
#--------------------------------------------------
#Device ID Code IR Length Part Name
# 1 4ba00477 4 arm_dap
# 2 23731093 6 xc7z045
# 3 4ba00477 4 arm_dap
# 4 1372c093 6 xc7z030
# ...
# 9 4ba00477 4 arm_dap
# 10 1372c093 6 xc7z030
#
# Scan the device chain to see how many carriers we have
set deviceChain [readjtagchain -cable url TCP:$TCP]
set lastDevice [string range $deviceChain [string last devicenr $deviceChain]+9 [string last devicenr $deviceChain]+10]
puts "last device in programming chain is number $lastDevice"
set nCarriers [expr ($lastDevice-2)/2]
puts "It appears that you have $nCarriers carriers connected."
# Program bit files
fpga -f bitfiles/ScrodRevB_b2tt_gigE_${SCROD_FW_VERSION}.bit -debugdevice deviceNr 2 -cable type xilinx_tcf url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq
for {set i 4} {$i <= $lastDevice} {incr i 2} {
#Lynn's speedup improvements
# fpga -f bitfiles/CarrierRevE_${CARRIER_FW_VERSION}.bit -debugdevice deviceNr $i -cable url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq
# fpga -f bitfiles/CarrierRevE_newGUI_PS_LaserTest_debug.bit -debugdevice deviceNr $i -cable url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq
#Laser Test Golden File below!!!
fpga -f bitfiles/CarrierRevE_newGUI_PS_LaserTest_nodebug.bit -debugdevice deviceNr $i -cable type xilinx_tcf url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq
}
# Program PS for SCROD
xload hw bitfiles/ScrodRevB_b2tt_gigE_${SCROD_FW_VERSION}.hdf
source bitfiles/ps7_init_SCROD.tcl
xconnect arm hw -cable type xilinx_tcf url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq -debugdevice devicenr 1 cpunr 1
set_cur_target 64
set_cur_system
xzynqresetstatus 64
ps7_init
ps7_post_config
xclearzynqresetstatus 64
xreset 64 0x80
dow ps_files/Scrod_PS_app_${SCROD_ELF_VERSION}.elf
xsafemode 64 off
con
# Program PS for carriers
for {set i 3} {$i < $lastDevice} {incr i 2} {
#Lynn's speedup improvements
# xload hw bitfiles/CarrierRevE_${CARRIER_FW_VERSION}.hdf
#Laser Test Golden File below!!!
xload hw bitfiles/CarrierRevE_newGUI_PS_LaserTest_debug.hdf
source bitfiles/ps7_init_CARRIER.tcl
xconnect arm hw -cable type xilinx_tcf url TCP:$TCP frequency $freq -debugdevice devicenr $i cpunr 1
set_cur_target 64
set_cur_system
xzynqresetstatus 64
ps7_init
ps7_post_config
xclearzynqresetstatus 64
xreset 64 0x80
dow ps_files/CarrierRevE_PS_app_${CARRIER_ELF_VERSION}.elf
xsafemode 64 off
con
}
|
| Attachment 18: setup_env_template.sh
|
#!/bin/bash -e
# written 2014-12-30 by mza
# last updated 2014-12-30
declare scriptdir=$(dirname "$BASH_SOURCE")
cd "${scriptdir}"
scriptdir="$(pwd -P)"
cd - >/dev/null
# Moved this script to a local dir
#declare otherscriptdir="${scriptdir}/../../../tags/2015-01.gigE-carrier-pre-screen"
. "detect_linux_variant" >/dev/null
function delete_boogers {
local string="${1}"
string=$(echo "${string}" | sed -e "s,^:,,")
string=$(echo "${string}" | sed -e "s,:$,,")
string=$(echo "${string}" | sed -e "s,::,:,g")
echo ${string}
}
function delete_repeats {
string=$(echo "${1}" | sed -e "s,:, ,g")
#echo ${string}
newstring=$( (for each in ${string}; do echo "${each}"; done; ) | sort -u)
newstring=$(echo $(echo "${newstring}") | sed -e "s, ,:,g")
echo ${newstring}
}
declare -i errors=0
declare BASE QTDIR PYTHONPATH
BASE="${PWD}"
if [ "$OS" = "Ubuntu" ]; then
if [ ${BITS} -eq 32 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/qt4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/qt4"
elif [ ${BITS} -eq 64 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4"
fi
elif [ "$OS" = "Linux" ]; then
if [ ${BITS} -eq 32 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/qt4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/lib/qt4"
elif [ ${BITS} -eq 32 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/qt4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/qt4"
elif [ ${BITS} -eq 64 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib64/qt4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/lib64/qt4"
elif [ -e "/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.6.4" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.6.4"
elif [ -e "/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.4.3" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.4.3"
elif [ -e "/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.8.5" ]; then
QTDIR="/usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.8.5"
fi
else
:
fi
#for each in "/usr/lib/qt4" "/usr/lib64/qt4" "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4" "/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/qt4"; do
if [ -z "${QTDIR}" ] || [ ! -e "${QTDIR}/bin/qmake" ]; then echo "error: is libqt4-dev installed?" > /dev/stderr; errors=$((errors+1)); fi
# || [ ! -e "${QTDIR}/lib" ]
#PATH="${QTDIR}/bin:${PATH}"
PATH="${BASE}/bin:${QTDIR}/bin:${PATH}"
#export PATH="${ROOTSYS}/bin:${PATH}"
PATH=$(delete_repeats ${PATH})
PATH=$(delete_boogers ${PATH})
PYTHONPATH="${BASE}/python/lib/python"
#PYTHONPATH="${BASE}/python/lib64/python"
# a xilinx-related entry in the original LD_LIBRARY_PATH causes problems with the QT build
if [ "$OS" = "Ubuntu" ]; then
if [ ${BITS} -eq 32 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu" ]; then
LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu"
elif [ ${BITS} -eq 64 ] && [ -e "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu" ]; then
LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu"
fi
elif [ "$OS" = "Linux" ]; then
if [ ${BITS} -eq 32 ]; then
LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/lib:${QTDIR}/lib"
else
LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/lib64:${QTDIR}/lib"
fi
elif [ "${OS:0:6}" = "CYGWIN" ]; then
LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/lib:${QTDIR}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}"
else
:
fi
#for each in "/lib" "/usr/lib" "/lib64" "/usr/lib64" "/usr/lib/x86_64" "/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu" "/lib/i386-linux-gnu"; do
#export setenv LD_LIBRARY_PATH="${ROOTSYS}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}"
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$(delete_repeats ${LD_LIBRARY_PATH})
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$(delete_boogers ${LD_LIBRARY_PATH})
echo "LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}"
function check_for {
#cygwin is /lib/libxml2.dll.a
if [ "${OS:0:6}" = "CYGWIN" ]; then
suffix="dll.a"
name="$1.$suffix"
else
suffix="so"
name="$1.$suffix"
fi
#echo $name
installable=$2
string=$(echo "${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}" | sed -e "s,:, ,g")
#lib=$(find ${string} 2>/dev/null | grep ${name} | grep $suffix$ | head -n 1)
#echo "${string}"
lib=$(find ${string} 2>/dev/null | grep ${name})
if [ ! -z "${lib}" ]; then
libdir=$(dirname "${lib}")
if [ -z "${libdir}" ]; then echo "error: is ${installable} installed?" > /dev/stderr; errors=$((errors+1)); fi
else
echo "error: is ${installable} installed?" > /dev/stderr
errors=$((errors+1))
fi
}
check_for "libxml2" "libxml2-dev"
check_for "libbz2" "libbz2-dev"
check_for "libz" "libz"
#echo "as root, do the following if not already done:"
#echo "cd /lib/i386-linux-gnu"
#echo "ln -s libz.so.1 libz.so"
#echo "BASE ${BASE}"
#echo "PYTHONPATH ${PYTHONPATH}"
echo " PATH=${PATH}" | tee ${scriptdir}/makeenv
echo "LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}" | tee -a ${scriptdir}/makeenv
echo " QTDIR=${QTDIR}" | tee -a ${scriptdir}/makeenv
echo | tee -a ${scriptdir}/makeenv
export BASE QTDIR PYTHONPATH PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH
if [ ${errors} -ne 0 ]; then
(echo; echo "errors encountered"; echo;) > /dev/stderr
# this trick from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2683279/how-to-detect-if-a-script-is-being-sourced :
return 2>/dev/null || exit 17
fi
|
| Attachment 19: XRM.bashrc
|
# System-wide .bashrc file for interactive bash(1) shells.
# To enable the settings / commands in this file for login shells as well,
# this file has to be sourced in /etc/profile.
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
[ -z "$PS1" ] && return
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, overwrite the one in /etc/profile)
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
# Commented out, don't overwrite xterm -T "title" -n "icontitle" by default.
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
#case "$TERM" in
#xterm*|rxvt*)
# PROMPT_COMMAND='echo -ne "\033]0;${USER}@${HOSTNAME}: ${PWD}\007"'
# ;;
#*)
# ;;
#esac
# enable bash completion in interactive shells
#if ! shopt -oq posix; then
# if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
# . /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
# elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
# . /etc/bash_completion
# fi
#fi
# sudo hint
if [ ! -e "$HOME/.sudo_as_admin_successful" ] && [ ! -e "$HOME/.hushlogin" ] ; then
case " $(groups) " in *\ admin\ *)
if [ -x /usr/bin/sudo ]; then
cat <<-EOF
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
EOF
fi
esac
fi
# if the command-not-found package is installed, use it
if [ -x /usr/lib/command-not-found -o -x /usr/share/command-not-found/command-not-found ]; then
function command_not_found_handle {
# check because c-n-f could've been removed in the meantime
if [ -x /usr/lib/command-not-found ]; then
/usr/lib/command-not-found -- "$1"
return $?
elif [ -x /usr/share/command-not-found/command-not-found ]; then
/usr/share/command-not-found/command-not-found -- "$1"
return $?
else
printf "%s: command not found\n" "$1" >&2
return 127
fi
}
fi
export XILINXD_LICENSE_FILE="${HOME}/Xilinx.lic"
. /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2014.4/settings64.sh
. /opt/Xilinx/SDK/2014.4/settings64.sh
export targetIP="192.168.10.61"
#export targetIP="192.168.10.82"
#export targetIP="192.168.10.101"
alias gige="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE/"
#alias spi="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/firmware/targets/CarrierPSCheckNew/CarrierPSCheckNew.sdk/spiTest"
alias fpga="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE; xmd -tcl program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl"
#alias xil_pp="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/firmware/targets/CarrierPSCheckNew; vivado CarrierPSCheckNew.xpr"
alias develTest="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE; . setup_env_template.sh; ./bin/develTest "'${targetIP}'
alias max="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE; . setup_env_template.sh; python ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE/scripts/max_power.py"
alias min="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE; . setup_env_template.sh; python ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE/scripts/min_power.py"
alias amp="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE; . setup_env_template.sh; python ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/gigE/software/gigE/scripts/amps_powered_but_disabled.py"
alias arp="arping -I eth4 "'${targetIP}'
alias develTest2="cd /home/idlab/LaserBranch/software/gigE/; source setup_env_template.sh; bin/develTest 192.168.10.61"
#alias develTest2="cd /home/idlab/LaserBranch/software/gigE/; source setup_env_template.sh; bin/develTest 192.168.10.89"
alias fpga2="cd /home/idlab/LaserBranch; xmd -tcl program-bit-and-elf-and-go.xmd.tcl"
alias gige2="cd /home/idlab/LaserBranch/software/gigE/; source setup_env_template.sh; cd ScriptsWithCarrierAddressing"
#export LD_PRELOAD="/home/idlab/build/usb-driver/libusb-driver.so"
export PATH
|
|
4
|
Sat May 7 20:52:24 2016 |
James Bynes III | Instructions | Plotting data from XRM boardstack |
The following package will allow you to parse binary data from TargetX and output pedestal subtracted plots as well as a separate pedestal subtract text file in tabbed column format.
You will need python, numpy, scipy, and matplotlib packages installed. If you don't have them already, they can be installed through terminal with the following line (in Debian or Ubuntu):
sudo apt-get install python-numpy python-scipy python-matplotlib
Extract package to $PWD/pnnl/data/ directory
After taking data from XRM boardstack run the following command:
*note* binfile must be in the same directory
python XRM_script.py <binfile> <# of carriers> <# of windows> <plot 1 or 0 (yes or no?)>
The script will automatically compile c code and take pedestals if needed
example: (2 carriers) (4 windows) (yes plot)
python XRM_script.py test_2.bin 2 4 1
test_2.bin in included in download package for testing
Outputs:
Folder plots/ -- All plots will be stored here
XRMdataExtractor -- Data extractor program
XRMpedExtractor -- Pedestal extractor program
XRM_dataheader_<filename>.txt -- Raw data header
XRM_data_<filename>.txt -- Raw data in tab column format
XRM_pedHeader_<filename>.txt -- Pedestal only data header
XRM_ped_<filename>.txt -- Pedestal only data in tab column format
XRM_<filename>_ped_subtracted.txt -- Pedestal subtracted data in tab column format |
| Attachment 1: XRMdataExtractor.tar.gz
|
|
5
|
Tue May 17 16:03:12 2016 |
Gary Varner | report | compilation log | Following up on James` suggestion, have posted transcript of compilation log below.
Not sure if there is anything should worry about here.
Strangely, the ton of warnings saw the first time I tried went away...
|
| Attachment 1: compile.txt
|
running build
running build_ext
building 'pythonDaq' extension
creating build
creating build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7
x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc -pthread -fno-strict-aliasing -DNDEBUG -g -fwrapv -O2 -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -fPIC -I../generic/ -I/usr/include/python2.7 -c pythonDaq.cpp -o build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7/pythonDaq.o
creating build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7
c++ -pthread -shared -Wl,-O1 -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functions -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functions -Wl,-z,relro -fno-strict-aliasing -DNDEBUG -g -fwrapv -O2 -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -fstack-protector --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -Wformat -Werror=format-security build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7/pythonDaq.o -lz -lm -lrt -o build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/pythonDaq.so
running install
running build
running build_ext
running install_lib
creating lib
creating lib/python
copying build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/pythonDaq.so -> ./lib/python
running install_egg_info
Writing ./lib/python/PackageName-1.0.egg-info
-rwxrwxr-x 1 xrm xrm 817014 May 18 10:59 bin/develTest
|
|
6
|
Wed May 18 01:13:55 2016 |
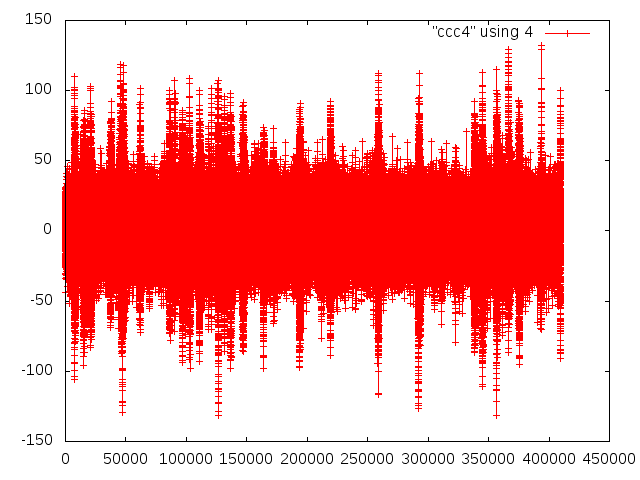
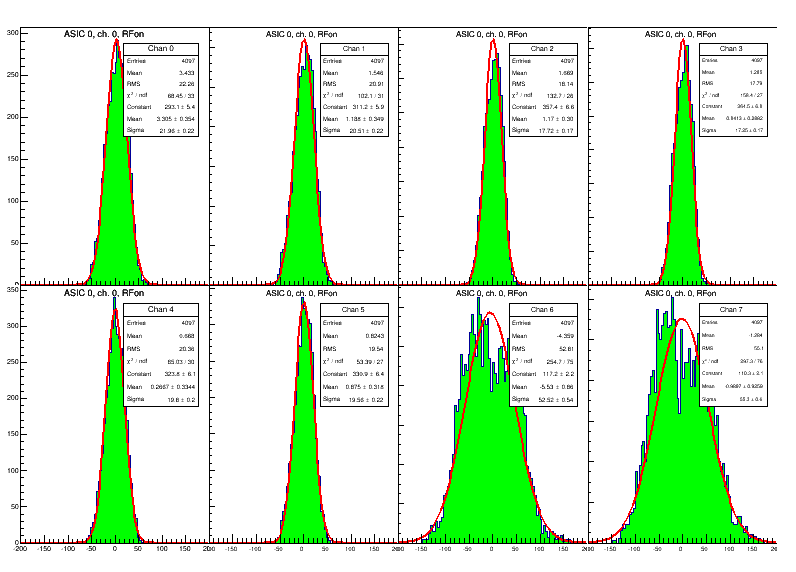
Chris Ketter, Gary Varner | analysis | first data sets | After getting data logging earlier in the day, Chris installed the detector and we took a look at data.
The amp board gain is set to lowest setting. Still, when looking at pedestal subtracted data, the preamps were picking up clear noise.
This may have impacted the pedestals, which were still noisy with preamps off, but long cables/detector connected.
Therefore cables disconnected, and noise demonstrated to be expected (Attachment 1). In this and subsequent plots, the x-axis sample number (approx 0.36ns/sample) and y-axis is ADC (roughly 1mV/count).
As a training exercise, Chris configured and logged these data sets.
Detector was reconnected and powered, with reference plots for ch0, ch1 in subsequent 2 attachments.
The noise is clearly correlated between channel pairs, as they are interleaved/looking at same signal.
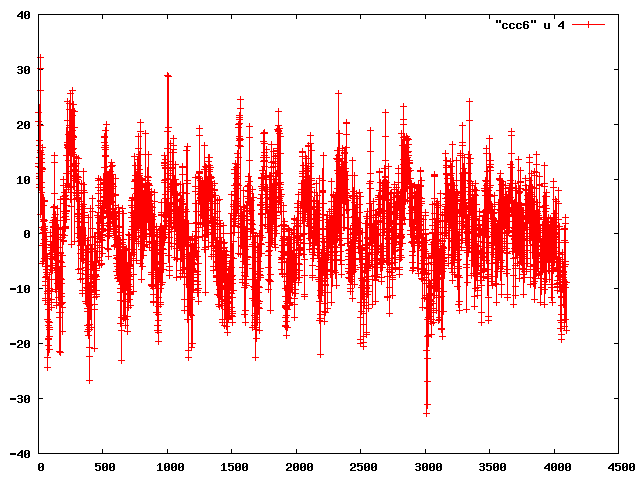
Looking at a different channel (ch6), the noise isn't so clearly correlated.
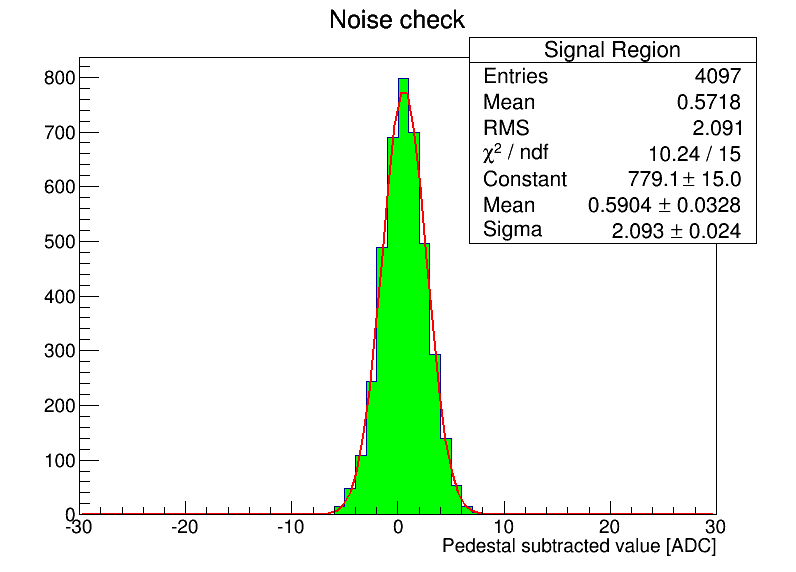
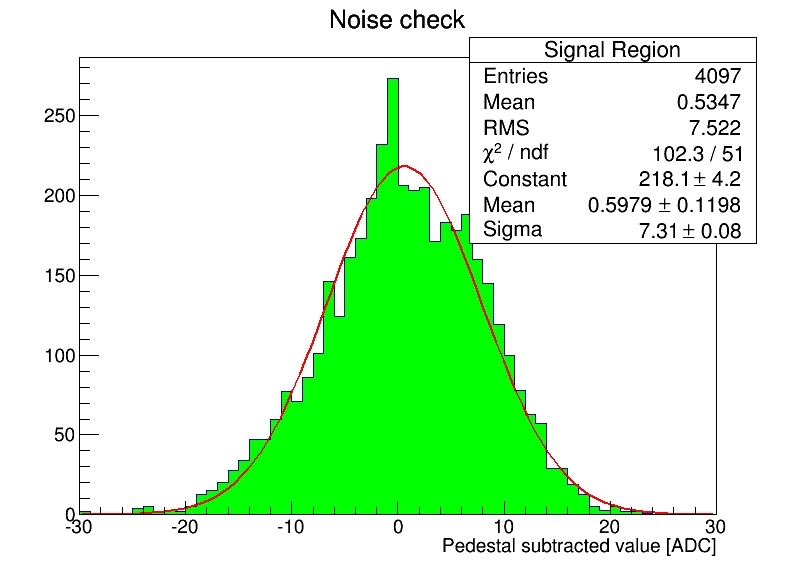
Because each trace is 4k samples, it is easy to focus on outliers, so a less biased approach is to look at the ensemble distributions.
An example of the two conditions for ch. 1 is posted as the last 2 plots, where the RMS spread is seen to increase from about 2 to 7 ADC counts RMS.
Interesting to compare values in the tunnel.
|
| Attachment 1: ch0_baseline.png
|
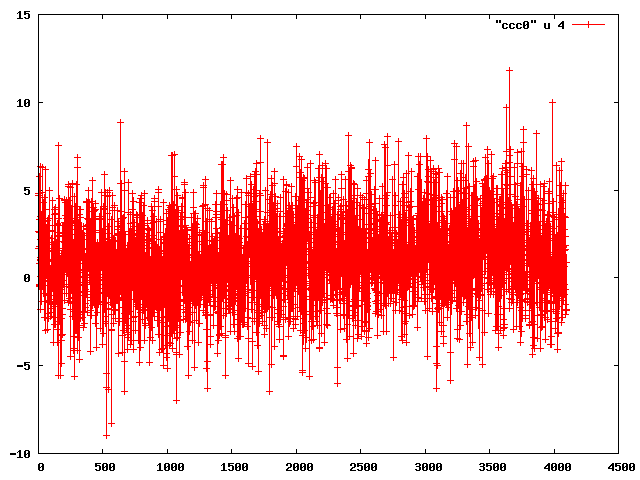
|
| Attachment 2: ch0_detAmp.png
|
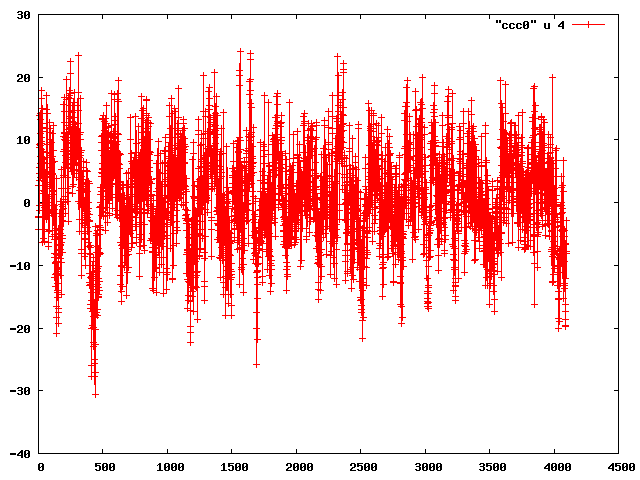
|
| Attachment 3: ch1_detAmp.png
|
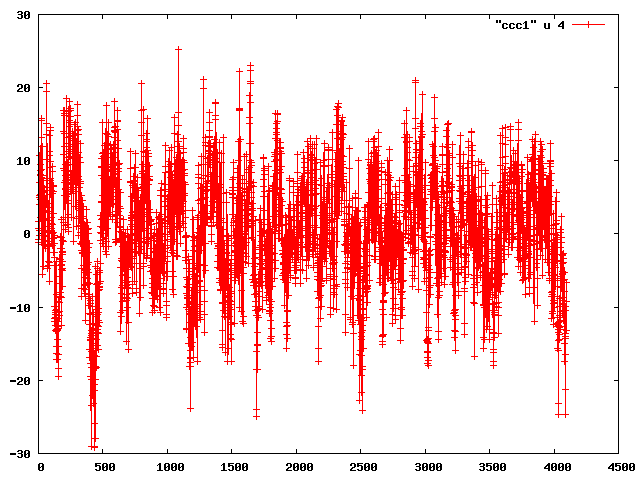
|
| Attachment 4: ch6_detAmp.png
|
|
| Attachment 5: ch1_distrib.png
|
|
| Attachment 6: ch1_distrib.png
|
|
|
7
|
Wed May 18 21:32:21 2016 |
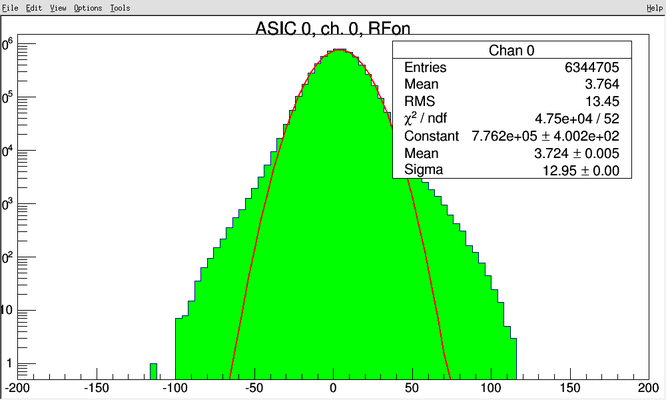
Gary Varner | noise during RF conditioning(?) | carrier 0, asic 0 | There is bursts of noise seen in the longer record lengths (1).
Some channels are quieter (2), though all see hints of 500MHz (3).
Channels 6&7 have pick-up that looks very much like 500MHz. (4).
Anyway, there is potentially good news here:
1) we aren`t completely deafened
2) a concurrent EMI baseline subtraction may be possible (use nominally unilluminated channel)
Key will be to see how large signal is.
|
| Attachment 1: ch4_RFon.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: ch4_RFon_4k.png
|
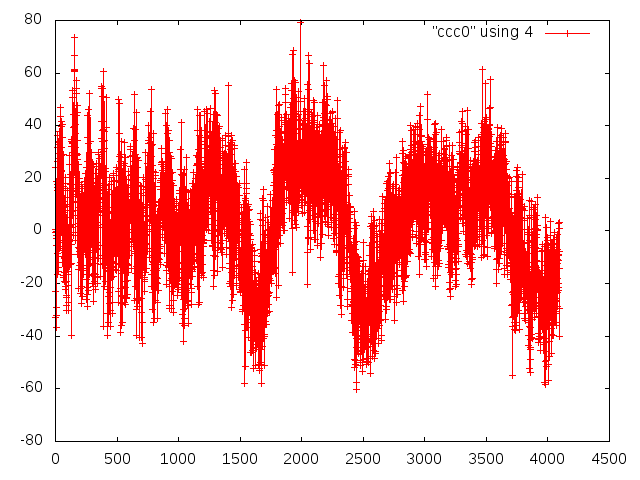
|
| Attachment 3: ch4_RFon_zoom.png
|
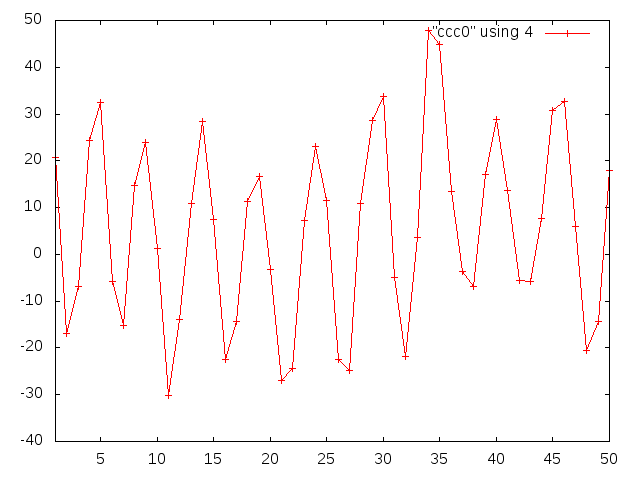
|
| Attachment 4: ch7_RFon_zoom.png
|
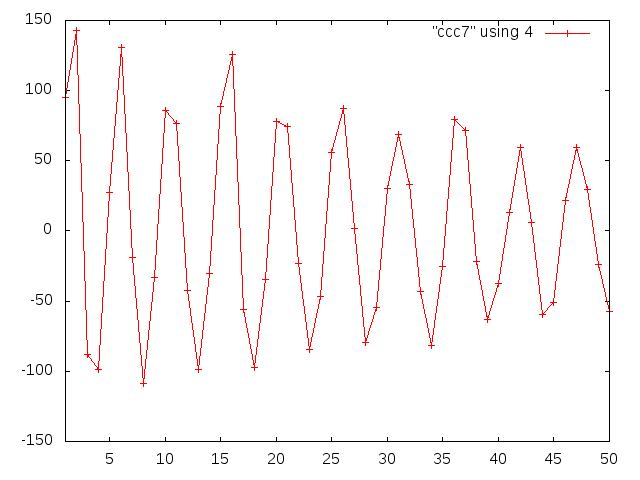
|
|
8
|
Thu May 19 02:08:09 2016 |
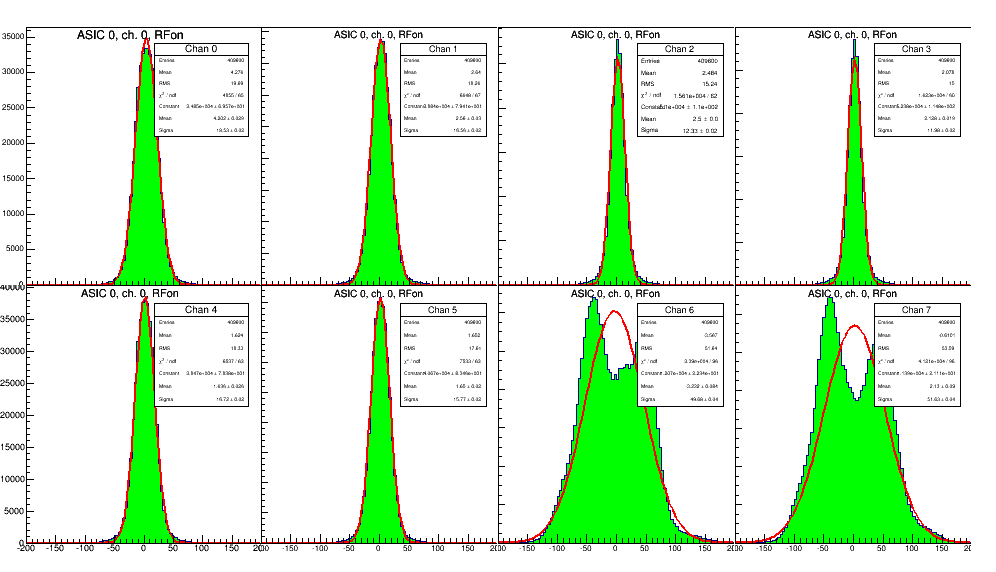
Gary Varner | analysis | statistics during RF on run | Summary statistics for short [1 run @ 64 windows] (1) and longer [100x] (2) show rather similar responses, where channels 6&7 are clearly noisier, while all others are in decent agreement.
It becomes clearer in the larger statistics that the distribution looks bimodal. This could be due to amplifier chain instability/oscillation.
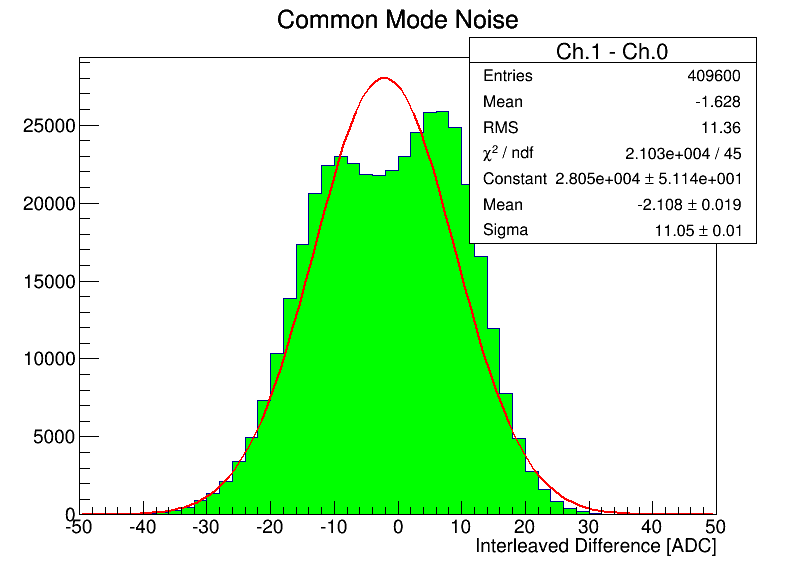
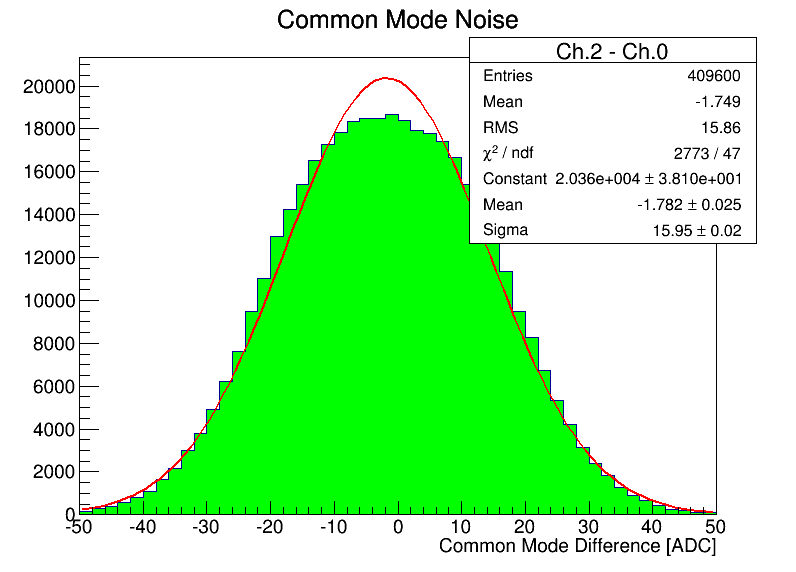
As a check of trying a common mode subtraction, did ch1-ch0 (3) and ch2-ch0 (4). In the first case this perhaps makes sense, if the signal is 500MHz, the phase difference leads to the difference seen. Should try to plot this modulo period and see if forms a periodogram. For channels that should be in phase, the improvement isn't as much as would think, so this needs further investigation. |
| Attachment 1: RFon_noiseSummary.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: RFon_noiseSummary.gif
|
|
| Attachment 3: InterleaveCMdiff.png
|
|
| Attachment 4: 2-0_CMdiff.png
|
|
|
9
|
Thu May 19 13:49:23 2016 |
Gary Varner | data taking problem report | morning 20-MAY-2016 JST | After beam came back on overnight, wanted to get a background reference data set.
However when trying to log data via GUI, the trigger number wasn't incrementing, nor a non-zero .bin file being created.
Restarted the GUI and confirmed that registers could be read, but still no response to triggers.
Tried selecting anoher ASIC and reconfig. Bricked the GUI. (Single Event Upset?)
Don't think bit file only FW reflash will work, but can try if unable to get power cycle of APC to work relatively soon.
Otherwise we are dead in the water. |
|
10
|
Thu May 19 19:48:14 2016 |
John Flanagan, Gary Varner | network documentation | APC network configuration |
host name : psxrd08
IP address : 172.19.62.89
MAC address: 00:c0:b7:b8:94:f9
> SuperKEKB ネットワーク 登録申請を受け付けました。
> ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
> 申請日 : 2016-05-19 15:49:00
> 申請内容 : 新規
> 登録者名 : フラナガン
> 登録者の所属 : Beam Monitor
> 電子メール : john.flanagan@kek.jp
> 機器の種類 : ネットワーク電源
> 使用OS :
> 設置場所 : D4,D8,トンネル内
> Host name : psxrd08
> DHCP server : Yes
> MAC address : 00-c0-b7-b8-94-f9
> VLAN : KEKB_CA_1
> 機器の使用用途 : x線モニター用
> その他 :
> ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
>
|
|
11
|
Thu May 19 23:01:35 2016 |
Gary Varner | analysis | first try | Started a 1Hz run and let it run, the tail end of which might have had the detector in the xray beam.
Stopped run, but the GUI crashed when trying to close the very large (>1.5k event) run.
Large files bit unwieldy to work with, but first time series plot for channel 0 attached (1).
And even more clearly, on log plot, can see nothing going on, so either had already crashed or was never in beam (2).
APC not making DHCP requests, so kinda stuck. |
| Attachment 1: ch0_timeseries.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: ch0_logPeds.png
|
|
|
12
|
Fri May 20 16:08:46 2016 |
John Flanagan, Gary Varner | hardware documentation | APC and PDU AC-power settings | Controlling remotely via separate laptop, with connections on the 2 subnets .0 and .1
APC is currently Default IP 192.168.1.201
apc/apc
LER PDU MAC:
00-06-18-75-4f-57
HER PDU MAC:
00-06-18-75-4f-10
Default IP:
192.168.0.216
user: snmp
pass: 1234
|
|
13
|
Fri May 20 23:30:23 2016 |
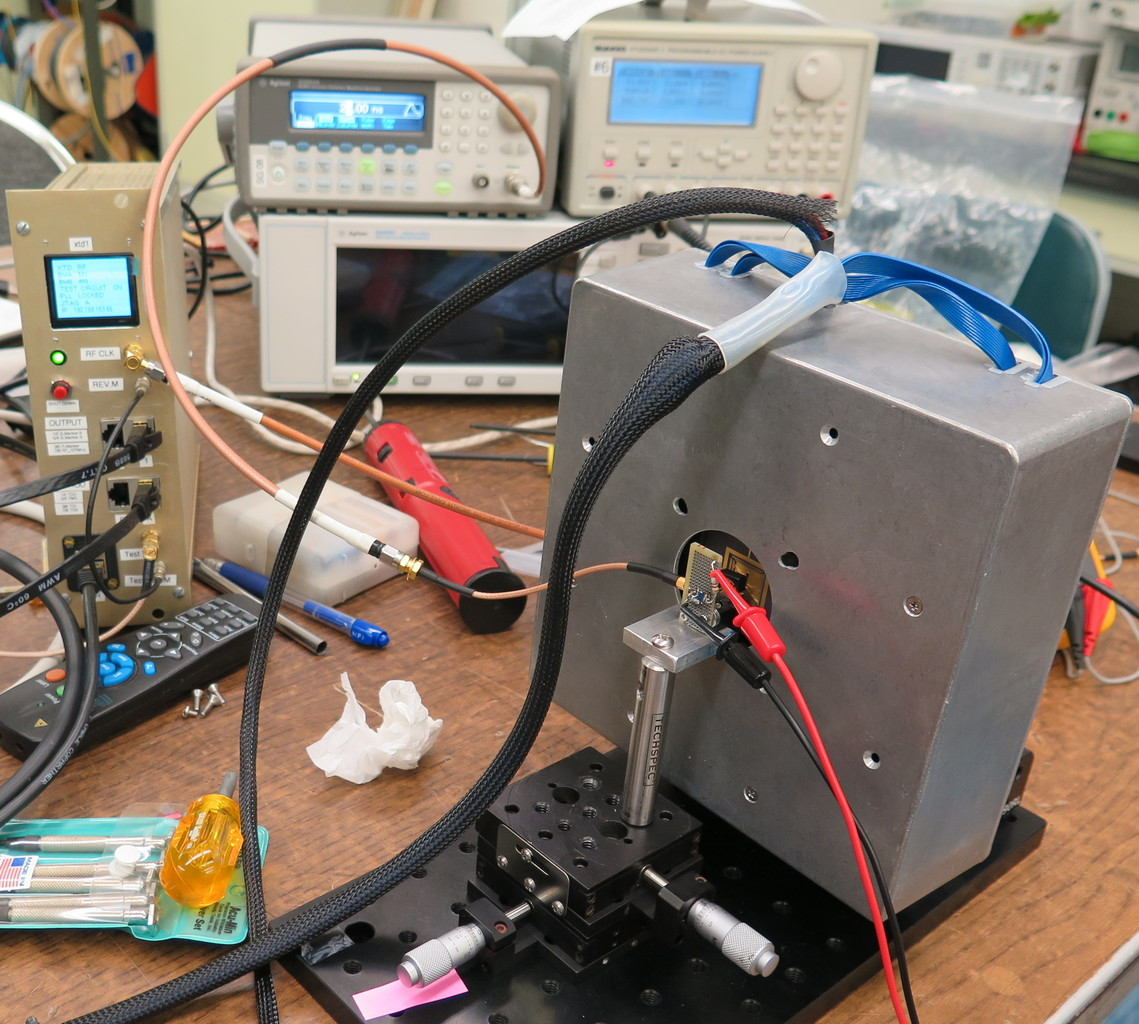
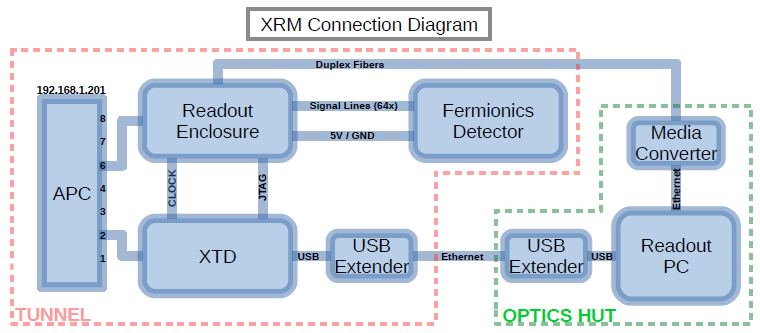
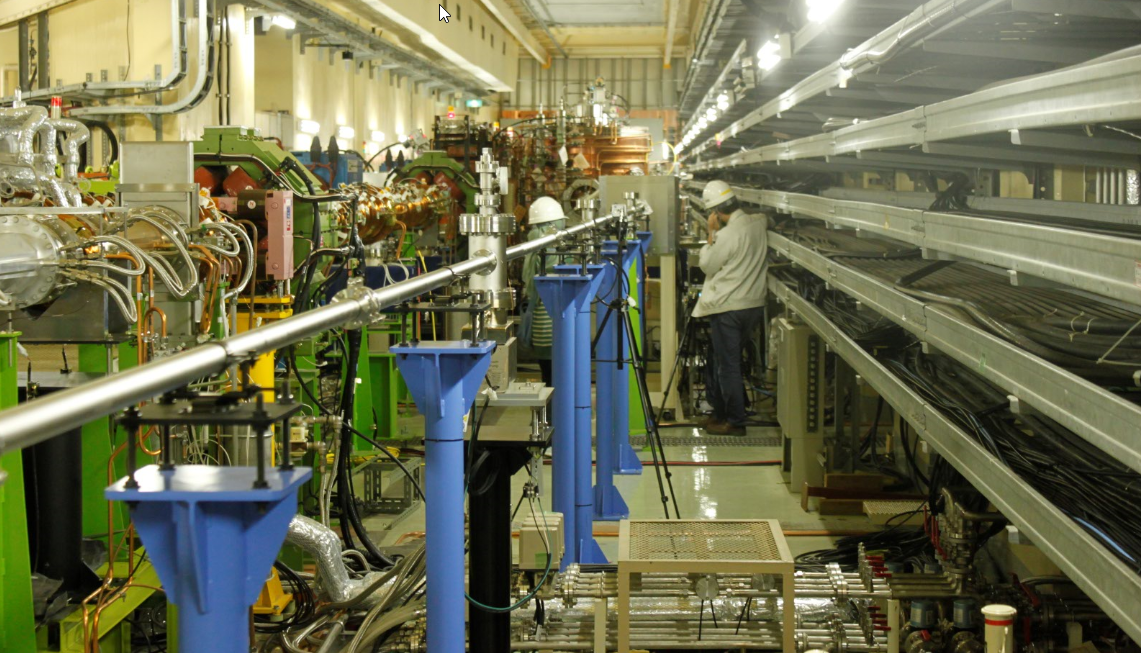
Chris Ketter | information | Configuration of XRM | Attachment 1 is a block diagram of the XRM setup for the Low Energy Ring (LER). Physically, this is located underneath the right wing of Fuji Hall, tens of meters away from the crossing point of the beams (180deg around ring from interaction point). Directly upstairs is the optics hut where the readout PC is located.
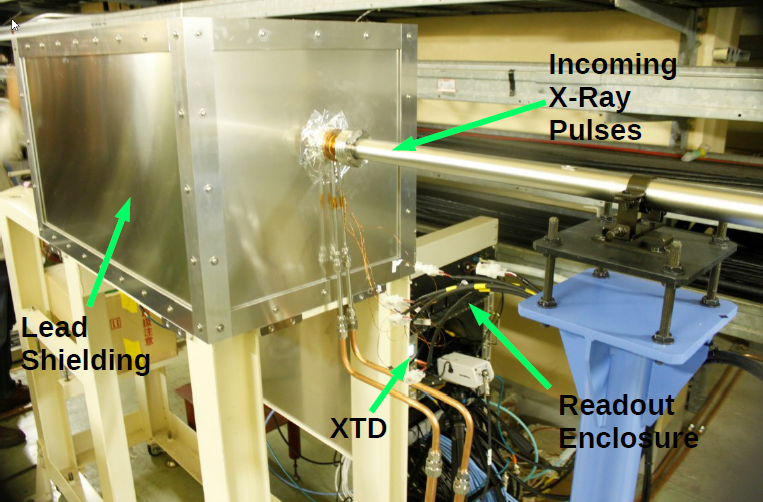
Attachment 2 details the physical location of all the components around the fermionics detector.
Attachment 3 is picture of the fermionics detector area from farther back.
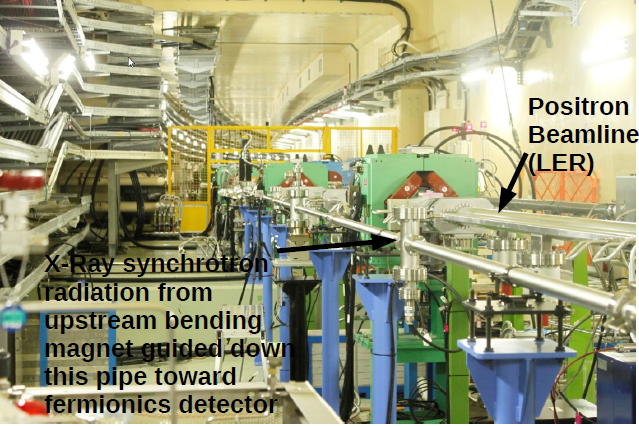
Attachment 4 shows (somewhat) the source of the X-Rays and the positron beam pipe from which they originate.
|
| Attachment 1: XRM_connection_diagram.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: XRM_detector.png
|
|
| Attachment 3: Xray_beamline.png
|

|
| Attachment 4: Xray_source.png
|
|
|
14
|
Sat May 21 01:02:13 2016 |
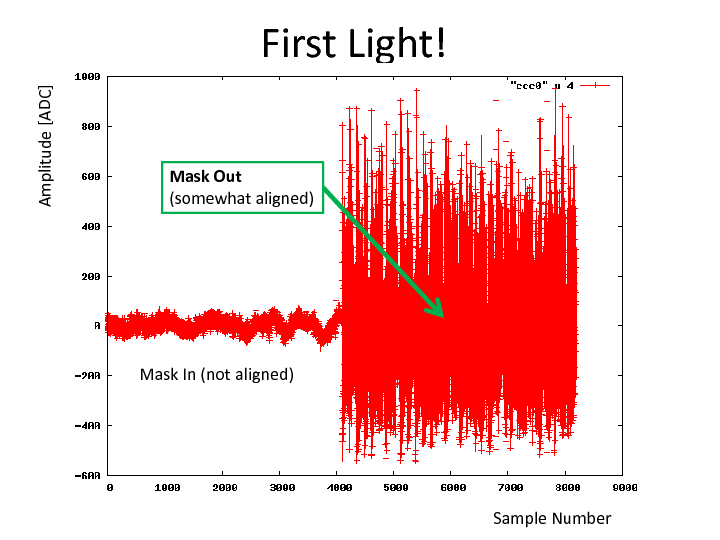
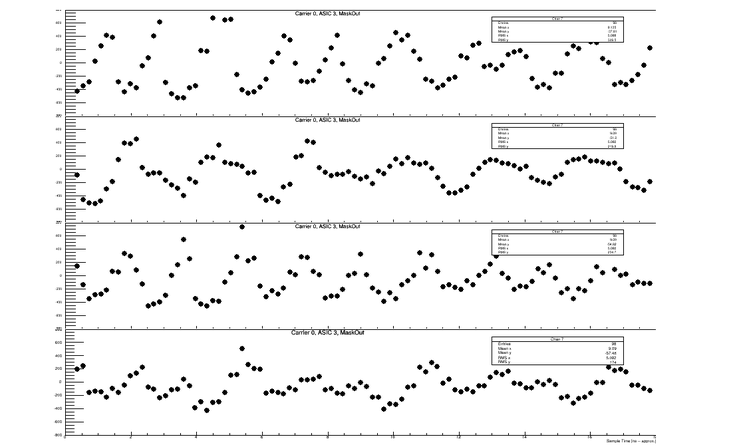
John Flanagan, Gary Varner | run report | First Light! | After a battle to sort out the networking issues with the APC (on loan) and PDU, able to get all working fine, and logged in separate Elog.
The ability to power cycle XRM proved essential as periodically something is happening in the tunnel which causes the network connections (both for XRM and APC) to get cycled.
While the APC can simply be logged into again, XRM requires a reprogram/reconfig cycle. Interestingly, the link comes back and registers can be read back.
But data taking/writes either are ignored or cause the link to become bricked. It could be an ARM stop, where some type of soft reset might work.
Anyway, without proper alignment fiducials, were scanning blind. To try and see something, the mask was removed. hitting the detector with ribbon of x-rays.
Clearly seen in the first attachment.
A zoom in for the 4 pixels being read is shown in the second attachment.
Obviously some signal processing is going to be needed to deal with the AC-coupled nature of this signal, and possibly induced ringing.
However the Signal-to-Noise is encouraging, as the amp board is running at minimal gain. |
| Attachment 1: firstLight_ch0.pdf
|
|
| Attachment 2: firstSamples.png
|
|
|
15
|
Tue Jan 22 07:56:56 2019 |
M. Andrew | documentation | instructions for setup, compiling and data acquisition | File XRM.instructions.txt gives the 2019-era details on running the XRM. |
| Attachment 1: XRM.instructions.txt
|
----------------------------- initial setup ---------------------------------
Put the following in ~/.bashrc:
export XILINXD_LICENSE_FILE="..."
. /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2014.4/settings64.sh > /dev/null
export url="https://www.phys.hawaii.edu/repos/belle2/itop/electronics"
alias repo="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo"
alias scrod="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/trunk/firmware/targets/ScrodRevB_b2tt"
alias carrier="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/trunk/firmware/targets/CarrierRevE"
alias mza="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/branches/mza/gigE"
alias sdev="cd ${HOME}/build/uh-svn-repo/trunk/software/b2l/scripts_dev"
then, do work in ~/build:
~/build$ svn checkout $url uh-svn-repo
the url for websvn (to do easy side-by-side comparisons of repo changes):
https://www.phys.hawaii.edu/websvn/wsvn/belle2/itop/electronics/
make the hostname of the data acquisition computer end in 3 digits (i.e. debian017; this is a workaround to be compatible with the belle2/TOP network setup)
And with the aliases above:
can go to the base of the repo with "repo"
can go to the location to compile the scrod firmware with "scrod"
can go to the location to compile the carrier firmware with "carrier"
can go to the location to program boardstack with "mza"
can go to the location to do configuration and readouts with "sdev"
------------------------------- compiling -----------------------------------
To compile firmware, you'll need to install xilinx vivado 2014.4
The changes needed right now for XRM (relative to a fresh checkout of the HEAD of the trunk of the TOP firmware) are:
changing three generics in the top scrod vhdl file:
trunk/firmware/targets/ScrodRevB_b2tt/hdl/ScrodRevB_b2tt.vhd
- IMPLEMENT_TRIGGER_STREAM_OUT_G : string := "Y"; -- "Y" or "N"
+ IMPLEMENT_TRIGGER_STREAM_OUT_G : string := "N"; -- "Y" or "N"
- DAQ_INTERFACE_G : string := "B2L"; -- "ETH" or "B2L"
+ DAQ_INTERFACE_G : string := "ETH"; -- "ETH" or "B2L"
- TT_LINK_TYPE_G : string := "B2TT"; -- "B2TT" or "XTDD"
+ TT_LINK_TYPE_G : string := "XTDD"; -- "B2TT" or "XTDD"
The bitfile version numbers should change to have a 0x0001 as the high 16 bits for XRM compiles, although so far not XRM bitfiles have been committed:
trunk/firmware/targets/ScrodRevB_b2tt/Version.vhd
-constant FPGA_VERSION_C : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := x"00000046"; -- MAKE_VERSION
+constant FPGA_VERSION_C : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := x"00010057"; -- MAKE_VERSION
To compile a new version of scrod or carrier firmware, do:
scrod
make # takes ~45 minutes
make elf # takes ~1 minute
carrier
make # takes ~25 minutes
make elf # takes ~1 minute
as a sidenote, you may have to issue "make gui" for each project at least once after a fresh checkout in order to get the "make elf" to successfully compile.
---------------------------- data acquisition -------------------------------
To program boardstacks, you'll need to install openocd-0.10 (compiled from source - the ubuntu package is not recent enough). There is a script to install openocd posted here:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mzandrew/bin/master/setup/as_you_like_it.openocd.sh
To do a check on collected pedestals, we use ROOT in our scripts, so make sure that is installed via:
sudo apt install root-system
alternately, can disable use of ROOT by setting use_gnuplot=1 in the file "trunk/software/b2l/scripts_rel/configure_boardstack_then_acquire_and_check_pedestals.sh"
So a typical flow is (after checkout):
repo
svn update
mza
./xrm.testing.sh # takes ~1 minute
sdev
./get_status.py # should report boardstack status
../scripts_rel/configure_boardstack_then_acquire_and_check_pedestals.sh a
|
|
16
|
Tue Jun 18 11:29:30 2019 |
M. Andrew | documentation | raspberry pi | to install:
cd
mkdir -p build
cd ~/build
git clone https://github.com/mzandrew/XRM.git
to run:
cd ~/build/XRM/predator
./get_temperatures.py # reads temps from SPI thermocouple
27.9 26.3
./read_serial.py # reads temp + ADC values from microcontroller for ammeter function
24.8 1.368 1.406
./take_pic.sh
./lights_on.sh
./lights_off.sh
./temperatures.sh # grabs snapshot of KEKB status and plots temperatures on it
./make_video.sh # makes video from individual images
./upload_to_samd21.sh # programs microcontroller (ADC for amplifier's ammeter)
./daemon.sh # started in /etc/rc.local upon bootup - runs in a loop once a minute: get_temperatures.py, read_serial.py and take_pic.sh
notes:
logfile for temperatures and voltages (for ammeter) is in logs/temperatures.log
latest picture is stored in pictures/picture.jpg; then archived with a date/time stamp in the filename (pictures/2019-06-13.105227.jpg)
|
|
17
|
Mon Sep 30 09:36:16 2019 |
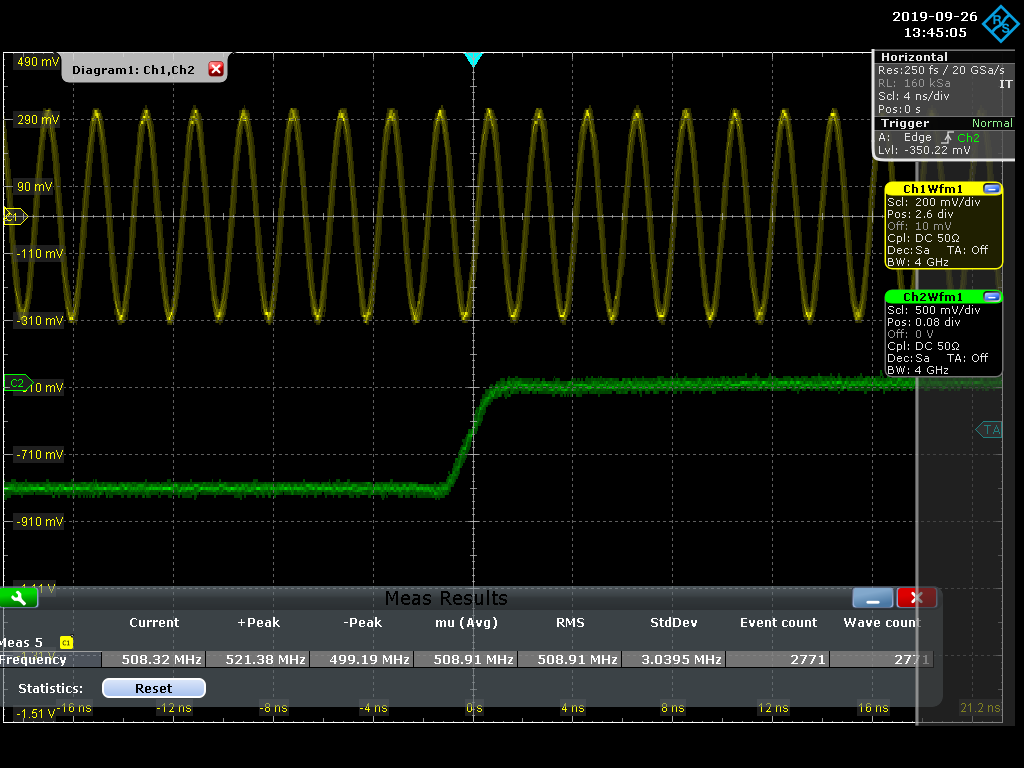
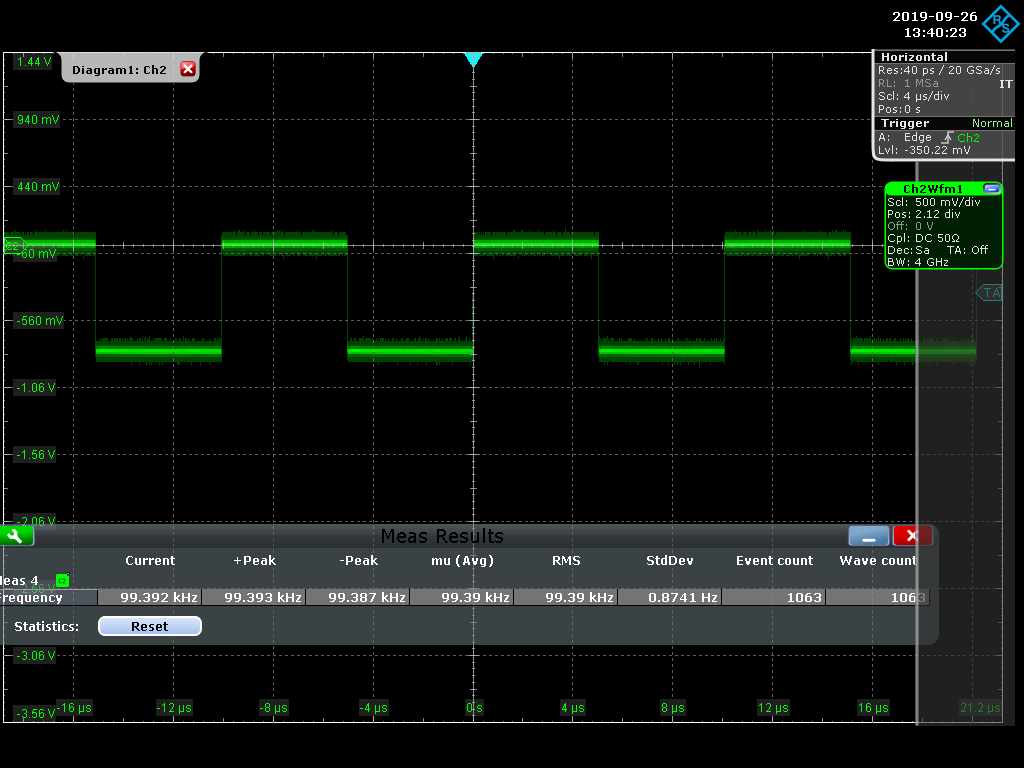
M. Andrew | documentation | measurements of accelerator clock and revolution marker | Following Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 499 (2003) 138–166, we know that the distributed accelerator clock is 508.8875 MHz (508.91 MHz measured) and that there are 5120 RF buckets. So the revolution marker should come at 99.3921 kHz (99.39 kHz measured).
Furthermore, it should be noted that the revolution marker is a 50% duty cycle NIM signal and the accelerator clock is about 600 mVpp. The RMS of the delay between an edge of the accelerator clock and the revolution marker is about 67 ps. These measurements were done in the D8 XRM optics hut (Oho) after the addition of cabling and RF/NIM fanout modules were inserted (but before the long cables down to the tunnel).
The scope used for the measurements was a Rhode & Schwartz RTO 1044. |
| Attachment 1: superkekb-accelerator-clock-frequency.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: superkekb-revolution-marker-frequency.png
|
|
| Attachment 3: delay-stability-of-accelerator-clock-edge-to-revolution-marker-edge.png
|
|
|
18
|
Mon Sep 30 10:59:35 2019 |
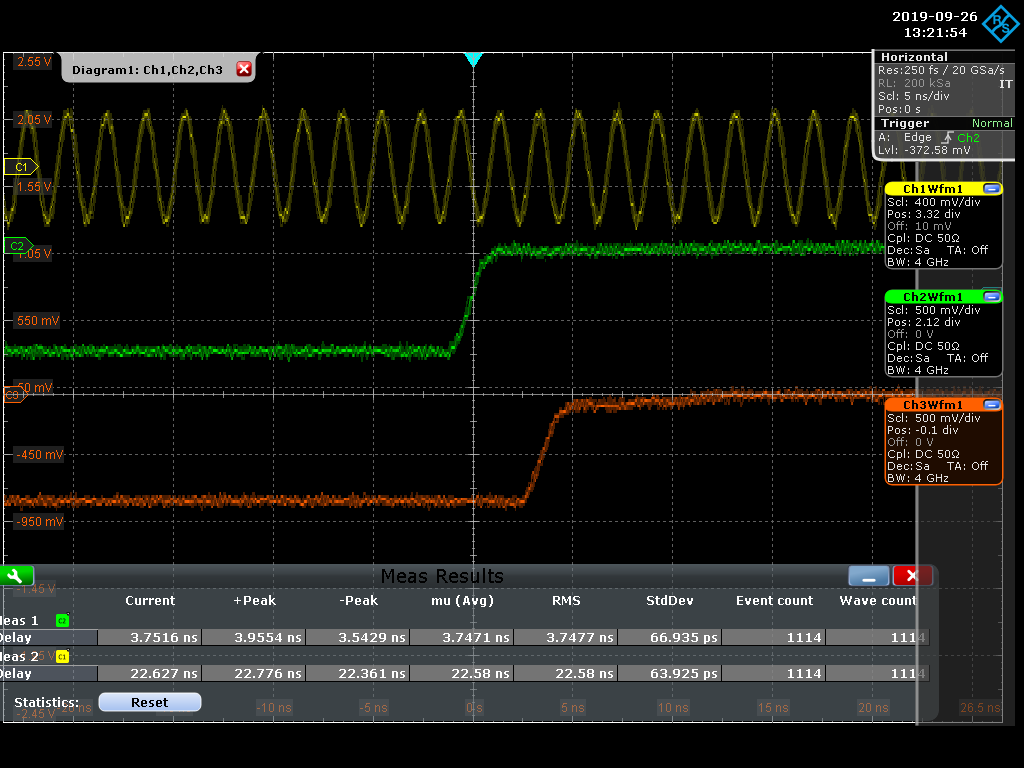
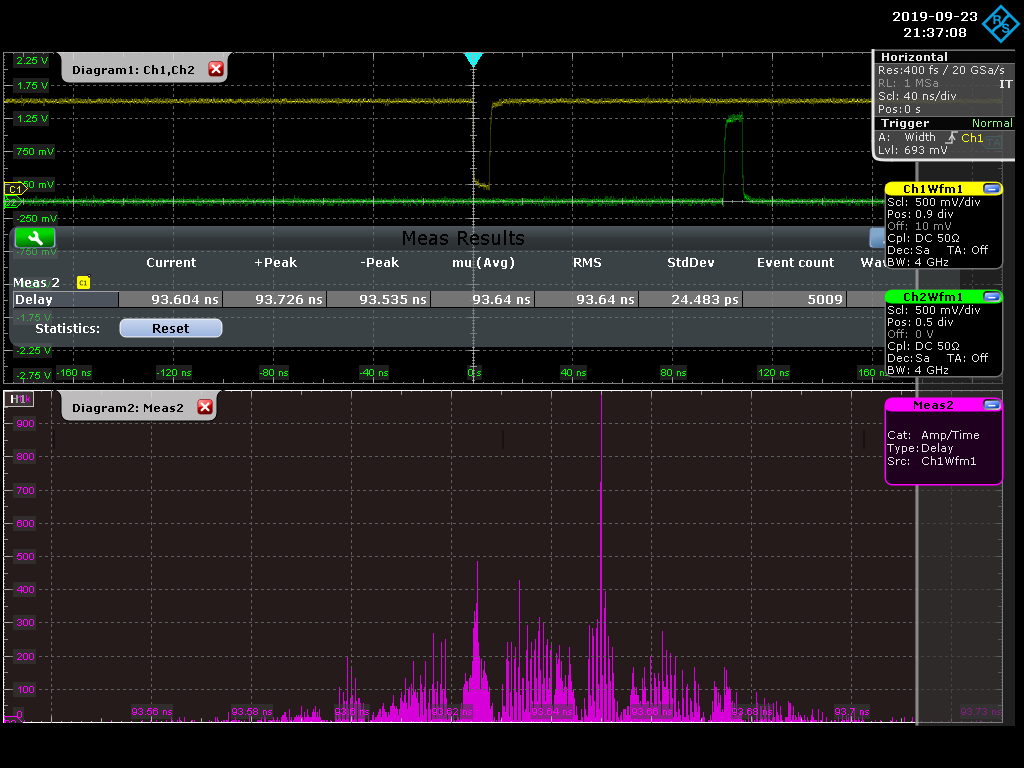
M. Andrew | documentation | Althea/RAFFERTY | The firmware running on Althea/RAFFERTY https://github.com/mzandrew/hdl/blob/master/verilog/src/mza-test032.pll_509divider_and_revo_encoder_plus_calibration_serdes.althea.v takes a 508.8875 MHz clock input, and uses a PLL to generate 4 phases of a 127.221875 MHz clock (input/4). Then it uses a 4-bit iserdes on the input clock to register the phase of the revolution marker on the output clock. It takes about 1 second worth of these and populates a histogram. Then it uses the most popular choice and outputs the corresponding phase of the 127 MHz so that the boardstack gets a revolution marker on that 127 MHz clock and the "bunch-0" happens during the first quarter of whichever 127 MHz clock the boardstack sees. This scheme *should* avoid having bunch-0 show up in a different quarter of the 127 MHz clock upon every power cycle.
The measured difference between revolution marker in from accelerator to revolution marker out to boardstack is 93.64 ns. This is measured on Althea/RAFFERTY in the D8 HER optics hut, but should be similar when in the tunnel because Althea/RAFFERTY has since been moved down there and the cable lengths after that are on the order of ~1 m. Overall delay from the accelerator revolution marker (in optics hut) to what Althea/RAFFERTY gets is still yet to be measured (and moreover what the phase of that is to when the synchrotron radiation from "bunch-0" goes through the HER He box). |
| Attachment 1: delay-from-revolution-marker-in-to-revo-out-to-boardstack.png
|
|
|
19
|
Fri Oct 4 08:55:23 2019 |
M. Andrew | documentation | instructions for pdu control | Control of the power distribution unit (pdu) is done from xrd04rp2. The script pdu.sh is in the $PATH.
to get pdu status:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ pdu.sh
[on] He box pwr
[off] Boardstack
0 W total
to power the boardstack on:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ pdu.sh on
[on] He box pwr
[on] Boardstack
50.0 W total
to turn the boardstack off:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ pdu.sh off
[on] He box pwr
[off] Boardstack
0 W total |
|
20
|
Fri Oct 4 10:04:12 2019 |
M. Andrew | documentation | instructions for programming boardstack | Programming the boardstack is done from xrd04rp2. The script boardstack.sh is in the $PATH.
To make sure the svn repo is up to date, run svnup.sh (also in $PATH) before programming:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ svnup.sh
Updating '.':
At revision 2869.
Program the boardstack:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ boardstack.sh
Open On-Chip Debugger 0.10.0+dev-00930-g09eb941c (2019-09-17-03:49)
Licensed under GNU GPL v2
For bug reports, read
http://openocd.org/doc/doxygen/bugs.html
Info : clock speed 6000 kHz
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.pl tap/device found: 0x23731093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x3731, ver: 0x2)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : carrier3.cpu.0: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier3.cpu.1: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier2.cpu.0: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier2.cpu.1: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier1.cpu.0: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier1.cpu.1: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier0.cpu.0: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : carrier0.cpu.1: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : SCROD.cpu.0: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : SCROD.cpu.1: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Info : Listening on port 3333 for gdb connections
Info : Listening on port 3334 for gdb connections
Info : Listening on port 3335 for gdb connections
Info : Listening on port 3336 for gdb connections
Info : Listening on port 3337 for gdb connections
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 8695644 Oct 4 2019 SCROD.bitfiles/ScrodRevB_b2tt_00010095.bit
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 3828341 Oct 1 07:35 carrier.bitfiles/CarrierRevE_00000062.bit
-rwxr-x--- 1 xrm idlab 239907 Sep 20 12:54 carrier.elffiles/CarrierRevE_PS_app_00000021.elf
-rwxr-x--- 1 xrm idlab 360637 Sep 17 05:56 SCROD.elffiles/Scrod_PS_app_0000006e.elf
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 20597 Sep 17 05:58 carrier.bitfiles/ps7_init.tcl
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 36137 Sep 17 05:57 SCROD.bitfiles/ps7_init.tcl
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 8695644 Oct 4 2019 SCROD.bitfiles/ScrodRevB_b2tt_00010095.bit
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 3828341 Oct 1 07:35 carrier.bitfiles/CarrierRevE_00000062.bit
programming bit file on SCROD...
programming bit file on carrier 0...
programming bit file on carrier 1...
programming bit file on carrier 2...
programming bit file on carrier 3...
-rwxr-x--- 1 xrm idlab 239907 Sep 20 12:54 carrier.elffiles/CarrierRevE_PS_app_00000021.elf
-rwxr-x--- 1 xrm idlab 360637 Sep 17 05:56 SCROD.elffiles/Scrod_PS_app_0000006e.elf
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 20597 Sep 17 05:58 carrier.bitfiles/ps7_init.tcl
-rw-r----- 1 xrm idlab 36137 Sep 17 05:57 SCROD.bitfiles/ps7_init.tcl
halting all the ARMs...
Error: Can't assert SRST: nSRST signal is not defined
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.pl tap/device found: 0x23731093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x3731, ver: 0x2)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Warn : carrier3.cpu.0: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier3.cpu.1: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier2.cpu.0: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier2.cpu.1: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier1.cpu.0: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier1.cpu.1: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier0.cpu.0: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : carrier0.cpu.1: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : SCROD.cpu.0: ran after reset and before halt ...
Warn : SCROD.cpu.1: ran after reset and before halt ...
Info : carrier3.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier3.cpu.0: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 0, multi core, no SMT
Info : carrier3.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier3.cpu.1: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 1, multi core, no SMT
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x000001d3 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x200001df pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier2.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier2.cpu.0: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 0, multi core, no SMT
Info : carrier2.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier2.cpu.1: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 1, multi core, no SMT
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x000001d3 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x200001df pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier1.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier1.cpu.0: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 0, multi core, no SMT
Info : carrier1.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier1.cpu.1: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 1, multi core, no SMT
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x000001d3 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x200001df pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier0.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier0.cpu.0: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 0, multi core, no SMT
Info : carrier0.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier0.cpu.1: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 1, multi core, no SMT
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x000001d3 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x200001df pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : SCROD.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : SCROD.cpu.0: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 0, multi core, no SMT
Info : SCROD.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : SCROD.cpu.1: MPIDR level2 0, cluster 0, core 1, multi core, no SMT
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x000001d3 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x200001df pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Error: Can't assert SRST: nSRST signal is not defined
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier3.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier2.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier1.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.pl tap/device found: 0x1372c093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x372c, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: carrier0.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.pl tap/device found: 0x23731093 (mfg: 0x049 (Xilinx), part: 0x3731, ver: 0x2)
Info : JTAG tap: SCROD.cpu tap/device found: 0x4ba00477 (mfg: 0x23b (ARM Ltd.), part: 0xba00, ver: 0x4)
Info : carrier3.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier3.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x00000193 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x2000019f pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier2.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier2.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x00000193 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x2000019f pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier1.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier1.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x00000193 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x2000019f pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : carrier0.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : carrier0.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x00000193 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x2000019f pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
Info : SCROD.cpu.0 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
Info : SCROD.cpu.1 rev 0, partnum c09, arch f, variant 3, implementor 41
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x00000193 pc: 0xffffff34
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
target halted in ARM state due to debug-request, current mode: System
cpsr: 0x2000019f pc: 0xffffff28
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
successful!
programming elf file on carrier0...
programming elf file on carrier1...
programming elf file on carrier2...
programming elf file on carrier3...
programming elf file on SCROD...
Note: If the boardstack is not powered, you will get many "Error: Invalid ACK (0) in DAP response" messages.
[optional] Then check how much power is being drawn:
xrm@xrd04rp2:~$ pdu.sh
[on] He box pwr
[on] Boardstack
80.0 W total |
|